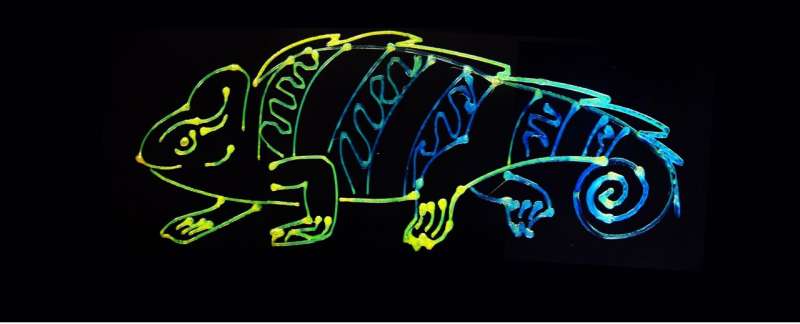
Chameleons inspire new multicolor 3D-printing technology (26/02/2024)
Inspired by the color-changing
ability of chameleons, researchers have developed a sustainable technique to
3D-print multiple, dynamic colors from a single ink.
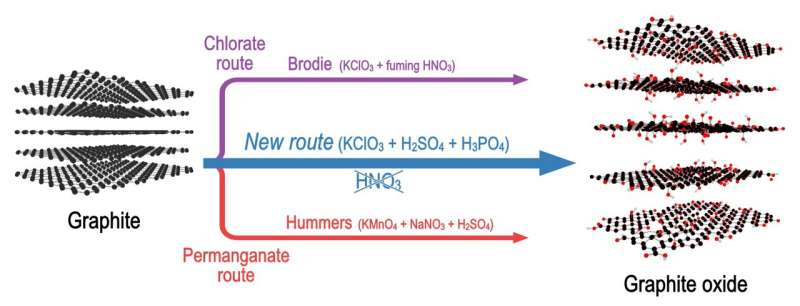
Research team introduces new non-toxic method for producing high-quality graphene oxide (26/02/2024)
Researchers from Umeå
University in Sweden have found a new way to synthesize graphene oxide, which
has significantly fewer defects compared to materials produced by the most
common method. Similarly good graphene oxide could be synthesized previously
only by using a rather dangerous method involving extremely toxic fuming nitric
acid.
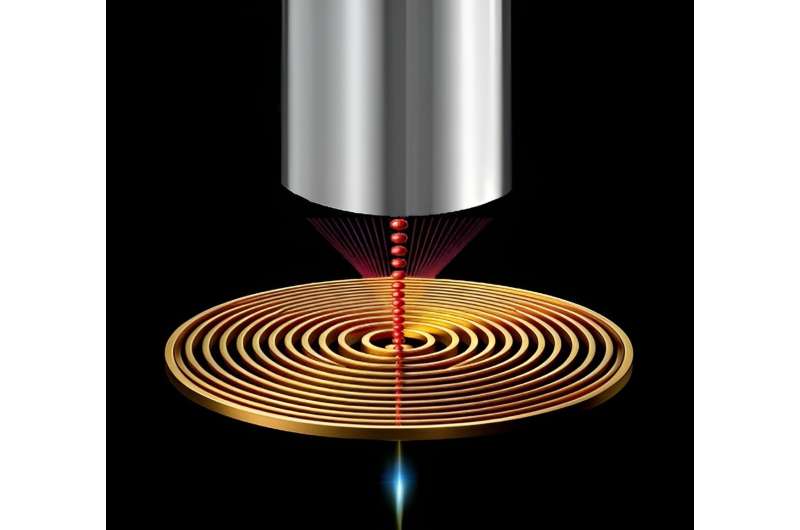
Breakthrough in single-photon integration holds promise for quantum computing, cryptography (23/02/2024)
A
recent study has unveiled a significant advancement toward the on-chip
integration of single-photon sources at room temperature. This achievement
represents a significant step forward in the field of quantum photonics and
holds promise for various applications, including quantum computing,
cryptography, and sensing.
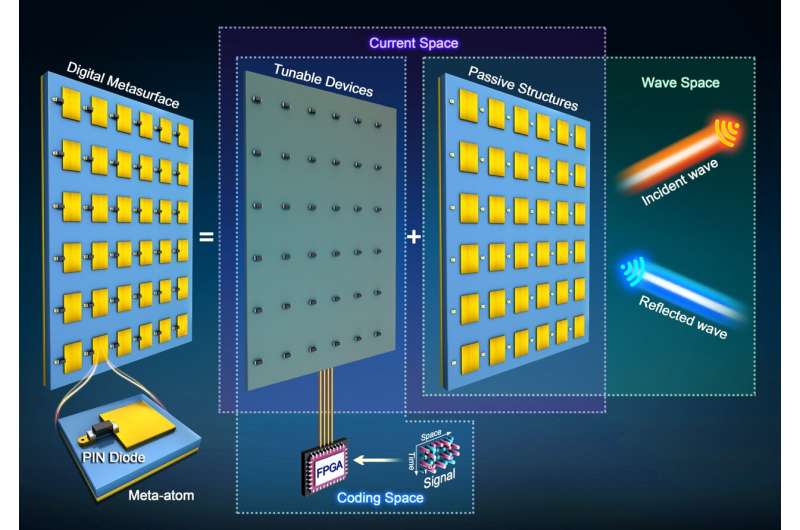
Accurate quantitative analysis of information loss from digital metasurfaces caused by mutual coupling (22/02/2024)
Research by Dr. Ruiwen Shao and Prof.
Junwei Wu (Institute of Electromagnetic Space, Southeast University, Nanjing,
China) teaches us about how digital metasurfaces lose information.
Engineers use AI to wrangle fusion power for the grid (22/02/2024)
In
the blink of an eye, the unruly, superheated plasma that drives a
fusion reaction can lose its stability and escape the strong magnetic fields
confining it within the donut-shaped fusion reactor. These getaways frequently
spell the end of the reaction, posing a core challenge to developing fusion as
a non-polluting, virtually limitless energy source.
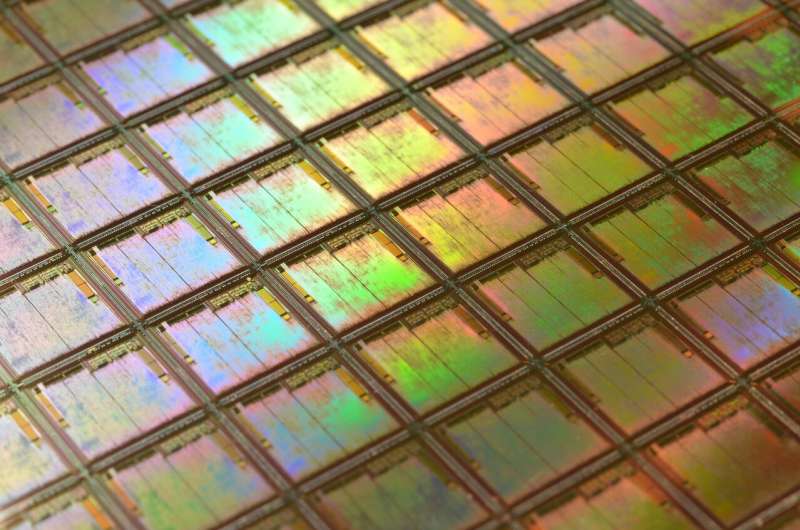
Plasma scientists develop computer programs that could reduce the cost of microchips, stimulate manufacturing (22/02/2024)
Fashioned
from the same element found in sand and covered by intricate patterns,
microchips power smartphones, augment appliances and aid the operation of cars
and airplanes.

A new phase of matter: Physicists achieve first demonstration of non-Abelian anyons in a quantum processor (22/02/2024)
Our
physical, 3D world consists of just two types of particles: bosons, which
include light and the famous Higgs boson; and fermions—the protons, neutrons,
and electrons that comprise all the "stuff," present company
included.
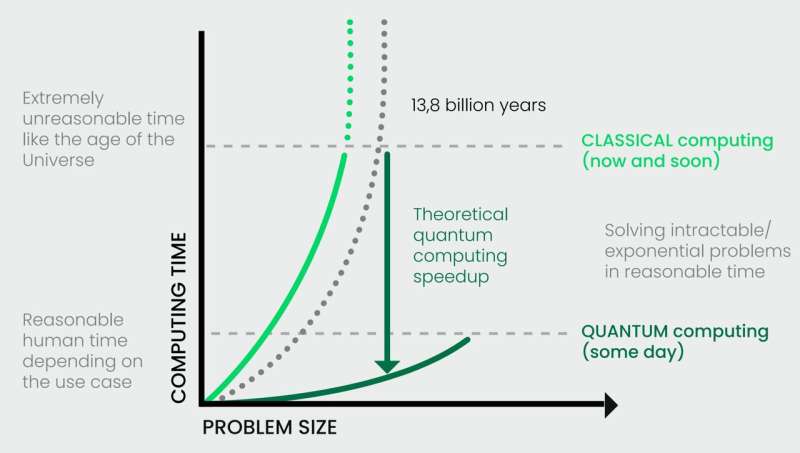
Developing doubly sustainable quantum computers (20/02/2024)
In the future, the use
of quantum computers could make a significant contribution to promoting greater
sustainability in global developments. This was shown in a white paper, which was recently presented at the UN Climate Change
Conference in Dubai and included contributions from the HPCQS consortium.
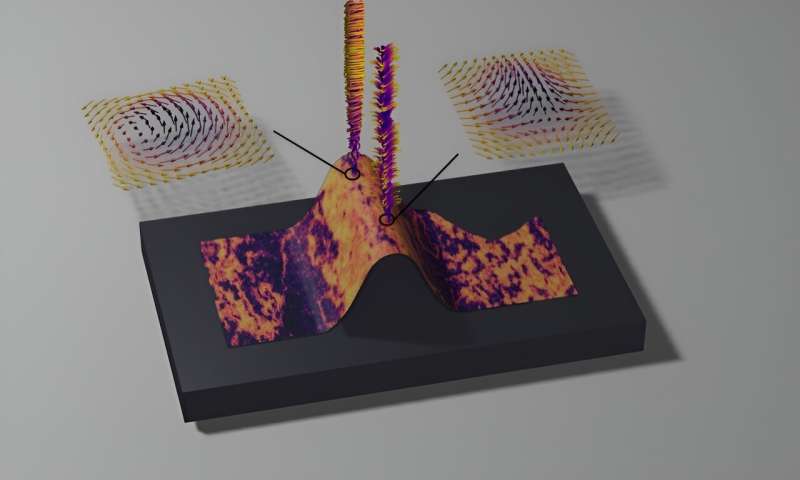
Researchers achieve breakthrough in silicon-compatible magnetic whirls (20/02/2024)
Researchers
from Oxford University's Department of Physics have made a breakthrough in
creating and designing magnetic whirls in membranes that can be seamlessly
integrated with silicon. These hurricane-like magnetic whirls, thought to move
at incredible speeds of up to kilometers per second could be used as
information carriers in a new generation of green and super-fast computing
platforms.
Physicists develop new solar cell design for better efficiency (20/02/2024)
Physicists
at Paderborn University have used complex computer simulations to develop a new
design for significantly more efficient solar cells than previously available.
A thin layer of organic material, known as tetracene, is responsible for the
increase in efficiency. The results have now been published in Physical
Review Letters.









