
Faster photons could enable total data security (19/07/2018)
Researchers
at the University of Sheffield have solved a key puzzle in quantum physics that
could help to make data transfer totally secure.
Artificial intelligence technology could help protect water supplies (19/07/2018)
Progress
on new artificial intelligence (AI) technology could make monitoring at water
treatment plants cheaper and easier and help safeguard public health.

Heat-conducting crystals could help computer chips keep their cool (12/07/2018)
As
consumers demand smaller, faster and more powerful electronic devices that draw
more current and generate more heat, the issue of heat management is reaching a
bottleneck. Researchers have created a potential solution -- boron arsenide
crystals with high thermal conductivity, which might be used in future
electronics to help keep devices from overheating.
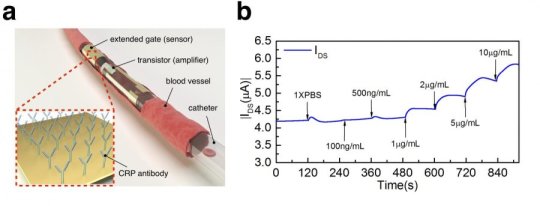
Ultra-thin sensor makes inflammation testing and curing 30 times faster (12/07/2018)
Researchers
have developed a real-time ultraflexible sensor that makes inflammation testing
and curing 30 times faster.

Training artificial intelligence with artificial X-rays (12/07/2018)
AI
holds real potential for improving both the speed and accuracy of medical
diagnostics -- but before clinicians can harness the power of AI to identify
conditions in images such as X-rays, they have to 'teach' the algorithms what
to look for. Now, engineers have designed a new approach: using machine
learning to create computer generated X-rays to augment AI training sets.

Qubits as valves: Controlling quantum heat engines (12/07/2018)
Researchers
are designing nano-sized quantum heat engines to explore whether they may be
able to outperform classical heat engines in terms of power and efficiency.

Physicists uncover why nanomaterial loses superconductivity (12/07/2018)
Physicists
have discovered that superconducting nanowires made of MoGe alloy undergo quantum
phase transitions from a superconducting to a normal metal state when placed in
an increasing magnetic field at low temperatures. The study is the first to
uncover the microscopic process by which the material loses its
superconductivity.

Breakthrough in construction of computers for mimicking human brain (12/07/2018)
A
computer built to mimic the brain's neural networks produces similar results to
that of the best brain-simulation supercomputer software currently used for
neural-signaling research. Tested for accuracy, speed and energy efficiency,
this custom-built computer named SpiNNaker, has the potential to overcome the
speed and power consumption problems of conventional supercomputers, with the
aim of advancing our knowledge of neural processing in the brain, including
learning and disorders such as epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease.

Quantum-enhanced sensing of magnetic fields (06/07/2018)
An
international team of physicists has demonstrated that algorithms and hardware
developed originally in the context of quantum computation can be harnessed for
quantum-enhanced sensing of magnetic fields.
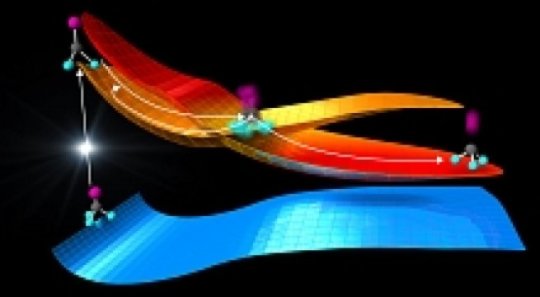
Ultra-high-speed 'electron camera' catches molecules at a crossroads (06/07/2018)
An
extremely fast 'electron camera' has produced the most detailed atomic movie of
the decisive point where molecules hit by light can either stay intact or break
apart. The results could lead to a better understanding of how molecules
respond to light in processes that are crucial for life, like photosynthesis
and vision, or that are potentially harmful, such as DNA damage from
ultraviolet light.









