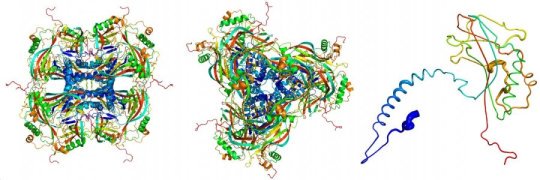
X-ray pulses reveal structure of viral cocoon (20/02/2017)
Scientists have used high-intensity
X-ray pulses to determine the structure of the crystalline protein envelope of
an insect virus. The tiny viruses with their crystal casing are by far the
smallest protein crystals ever analyzed using X-ray crystallography. This opens
up new opportunities in the study of protein structures.
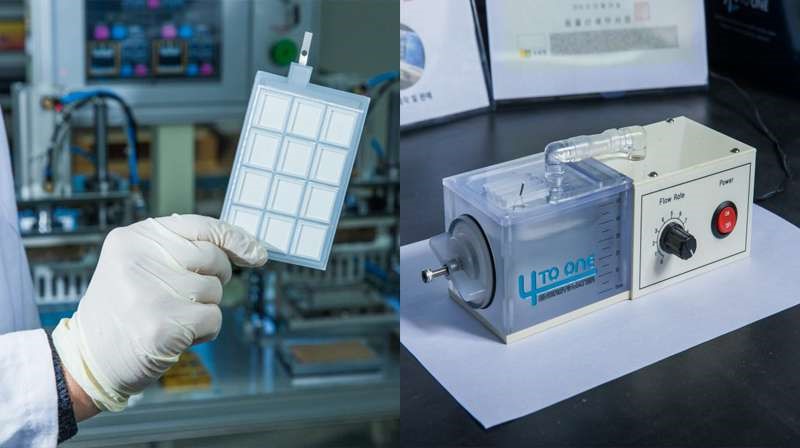

New eco-battery that runs on seawater (17/02/2017)
Researchers at Ulsan National
Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in South Korea will be working to
develop a new battery, using abundant and readily available seawater.
How water can split into two liquids below zero (16/02/2017)
Did
you know that water can still remain liquid below zero degrees Celsius? It is
called supercooled water and is present in refrigerators. At even smaller
temperatures, supercooled water could exist as a cocktail of two distinct
liquids. Unfortunately, the presence of ice often prevents us from observing
this phenomenon. So physicists had the idea of replicating the tetrahedral
shape of water molecules and thus removing the interference of ice formation.
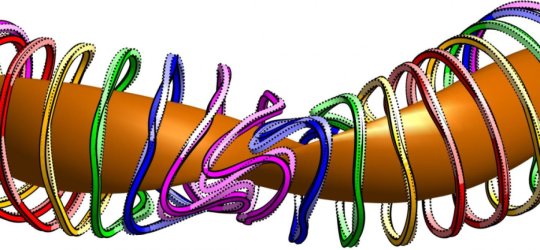
Physicist improves method for designing fusion experiments (14/02/2017)
A physicist has made an important
revision to a software tool used to design fusion experiments known as
stellarators. The new method results in designs that create a magnetic field
suitable for confining blazing-hot plasma, while allowing better access for
repairs and more places to install sensors.

The ultimate green technology: Creating computers that use 10,000 times less energy (14/02/2017)
Imagine patterning and visualizing
silicon at the atomic level, something which, if done successfully, will
revolutionize the quantum and classical computing industry. A team of
scientists has done just that, led by a world-renowned physicist and his
up-and-coming protégé.
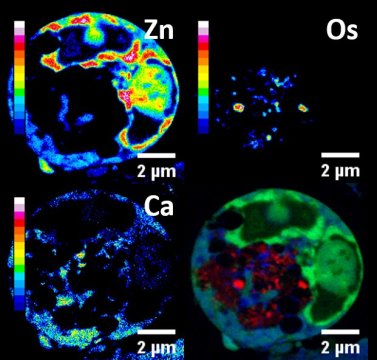
Organo-metal compound seen killing cancer cells from inside (14/02/2017)
Cancer cells have been observed being
targeted and killed from the inside with metal-based compound, report
researchers. The compound, Organo-Osmium FY26, attacks the weakest part of
cancer cells. FY26 is 50x more active than metal drugs used in current cancer
treatments, say researchers.
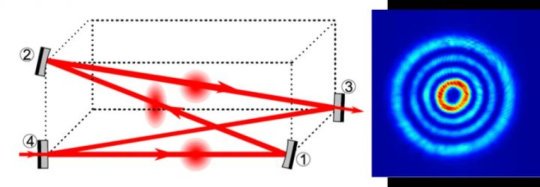
Increasing the sensitivity of next-generation gravitational wave detectors (14/02/2017)
Nearly one year ago today, the LIGO
Collaboration announced the detection of gravitational waves, once again
confirming Einstein's theory of General Relativity. This important discovery by
the Advanced Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (aLIGO) has
spurred great interest in improving these advanced optical detectors. The
mission of gravitational wave scientists worldwide is to make gravitational
wave detection a routine occurrence. Scientists from the institute that
developed the lasers used in Advanced LIGO have made significant progress to
support that goal.

Protecting bulk power systems from hackers (11/02/2017)
Most of us take turning the lights on
for granted. In reality, the energy we draw from the electrical grid to
brighten homes, freeze food and watch TV is part of a complicated and
widespread system. Understanding that system's vulnerabilities and reliability
is a crucial step towards improving its security.
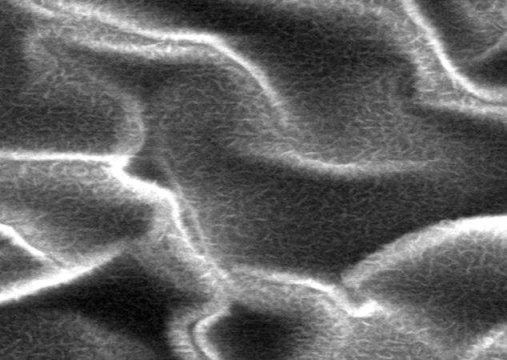
Nano-level lubricant tuning improves material for electronic devices and surface coatings (11/02/2017)
Researchers have developed a new
approach to dynamically tune the micro- and nano-scale roughness of atomically
thin MoS2, and consequently the appropriate degree of hydrophobicity for
various potential MoS2-based applications.

New, long-lasting flow battery could run for more than a decade with minimum upkeep (10/02/2017)
A new flow battery has been developed
that stores energy in organic molecules dissolved in neutral pH water. This new
chemistry allows for a non-toxic, non-corrosive battery with an exceptionally
long lifetime and offers the potential to significantly decrease the costs of
production.









