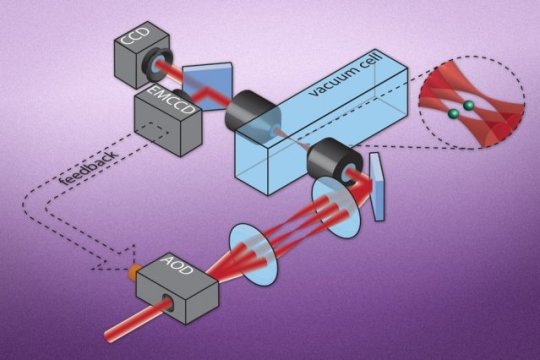
Scientists set traps for atoms with single-particle precision (04/11/2016)
Researchers report a new method to use
lasers as optical "tweezers" to pick individual atoms out from a
cloud and hold them in place. As the atoms are "trapped," the
scientists use a camera to create images of the atoms and their locations.
Based on these images, they then manipulate the angle of the laser beams, to
move individual atoms into any number of different configurations.

Flexible solar panel goes where silicon can't (04/11/2016)
A team of engineers and chemists is
producing flexible solar panels that can become part of window shades or
wallpaper that will capture light from the sun as well as light from sources
inside buildings.

Physicists demonstrate existence of new subatomic structure (04/11/2016)
Iowa State University researchers have
helped demonstrate the existence of a subatomic structure once thought unlikely
to exist.
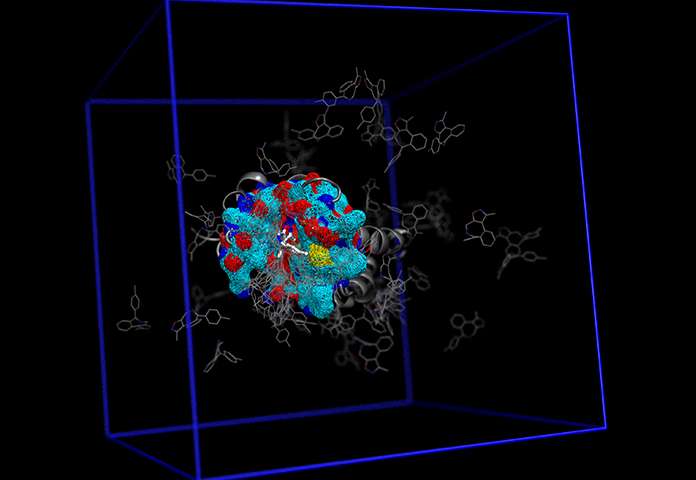
New computational tool may speed drug discovery (04/11/2016)
A new computational tool called
fABMACS is helping scientists see beyond static images of proteins to more
efficiently understand how these molecules function, which could ultimately
speed up the drug discovery process.

James Webb Telescope, now complete, countdown to launch begins (04/11/2016)
The biggest space telescope ever built is now complete
despite previous financial setbacks and delays. After testing it is expected to
launch in 2018.

Nanobionic spinach plants can detect explosives (02/11/2016)
Spinach is no longer just a superfood:
By embedding leaves with carbon nanotubes, engineers have transformed spinach
plants into sensors that can detect explosives and wirelessly relay that
information to a handheld device similar to a smartphone.

Next-generation smartphone battery inspired by the gut (02/11/2016)
A new prototype of a lithium-sulphur
battery -- which could have five times the energy density of a typical
lithium-ion battery -- overcomes one of the key hurdles preventing their
commercial development by mimicking the structure of the cells which allow us
to absorb nutrients.

New instrument could search for signatures of life on Mars (02/11/2016)
A sensing technique that the U.S.
military currently uses to remotely monitor the air to detect potentially
life-threatening chemicals, toxins, and pathogens has inspired a new instrument
that could "sniff" for life on Mars and other targets in the solar
system -- the Bio-Indicator Lidar Instrument, or BILI.
Technique reveals the basis for machine-learning systems' decisions (02/11/2016)
In recent years, the best-performing
systems in artificial-intelligence research have come courtesy of neural
networks, which look for patterns in training data that yield useful
predictions or classifications. A neural net might, for instance, be trained to
recognize certain objects in digital images or to infer the topics of texts.

Data analysis—and particularly
big-data analysis—is often a matter of fitting data to some sort of
mathematical model. The most familiar example of this might be linear
regression, which finds a line that approximates a distribution of data points.
But fitting data to probability distributions, such as the familiar bell curve,
is just as common.









