
A
team of researchers from the Instituto de Carboquímica of the Spanish National
Research Council (CSIC) has made a remarkable step forward in the development
of efficient and sustainable electronic devices. They have found a special
combination of two extraordinary nanomaterials that successfully results in a
new hybrid product capable of turning light into electricity, and vice-versa,
faster than conventional materials.
Researchers put a new twist on graphite (20/07/2023)
For
decades, scientists have been probing the potential of two-dimensional
materials to transform our world. 2D materials are only a single layer of atoms
thick. Within them, subatomic particles like electrons can only move in two
dimensions. This simple restriction can trigger unusual electron behavior,
imbuing the materials with "exotic" properties like bizarre forms of
magnetism, superconductivity and other collective behaviors among electrons—all
of which could be useful in computing, communication, energy and other fields.
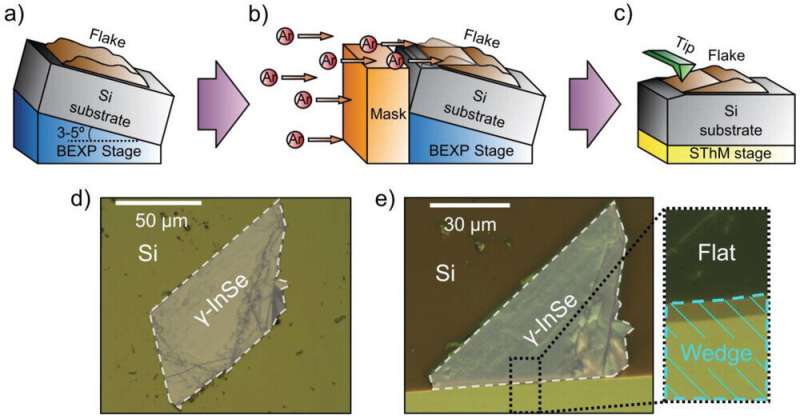
Highlighting an 'innovative approach' to research into 2D materials (20/07/2023)
New research from Lancaster
University presents an "innovative approach" to investigating the
heat conductivity of novel two-dimensional materials. The work paves the way
for creating efficient waste heat scavengers that generate cheap electricity,
new compact fridges, and advanced optical and microwave sensors and cameras.

Protons set to power next-generation memory devices (19/07/2023)
A
proton-driven approach that enables multiple ferroelectric phase transitions
sets the stage for ultralow power, high-capacity computer chips.
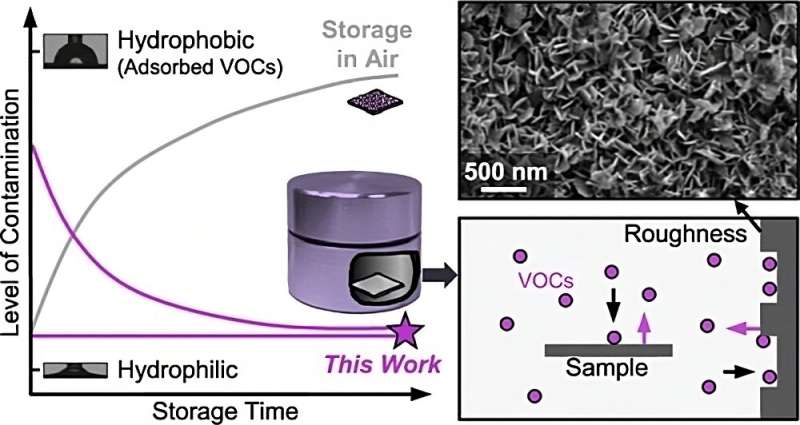
New storage technology keeps nanosurfaces clean (19/07/2023)
Rice University engineers have
created containers that can keep volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from
accumulating on the surfaces of stored nanomaterials.
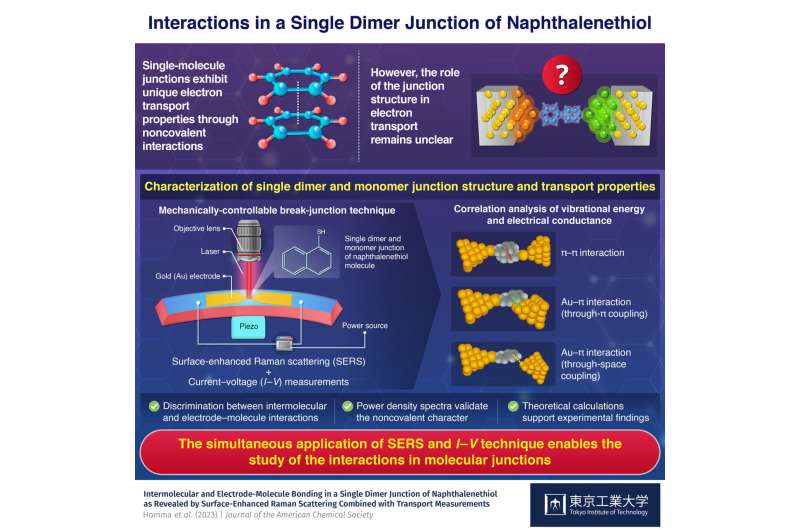
Investigating interactions at molecular junctions for novel electronic devices (17/07/2023)
The structure of a molecular
junction with noncovalent interaction plays a key role in electron transport,
reveals a recent study conducted by researchers at Tokyo Tech. Through
simultaneous surface-enhanced Raman scattering and current–voltage measurements,
they found that a single dimer junction of naphthalenethiol molecule shows
three different bondings, namely π–π intermolecular and through-π and
through-space molecule–electrode interactions.
New breakthrough shows how short pulses of light destroy particles (14/07/2023)
Polaritons are a peculiar state,
a kind of quasi-particles consisting of part-light and part-matter that can
bring unexpected abilities to conventional chemical reactions. New research
from Umeå University and others reveals that when the polaritons are hit by
very short pulses of light they collapse, and from then the reaction will be
completely controlled by conventional electronic transitions. The study is
published in Nature Communications.
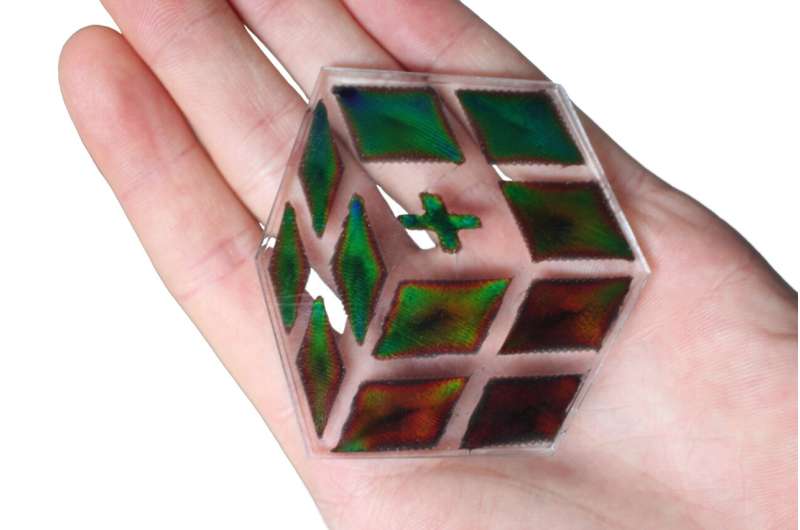

Researchers create 3D printed, biodegradable, color-changing conductive material from cellulose (14/07/2023)
An elastic material that changes
color, conducts electricity, can be 3D printed and is also biodegradable? That
is not just scientific wishful thinking: Empa researchers from the Cellulose
& Wood Materials laboratory in Dübendorf have produced a material with
these exact properties on the basis of cellulose and carbon nanotubes. The work
is published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
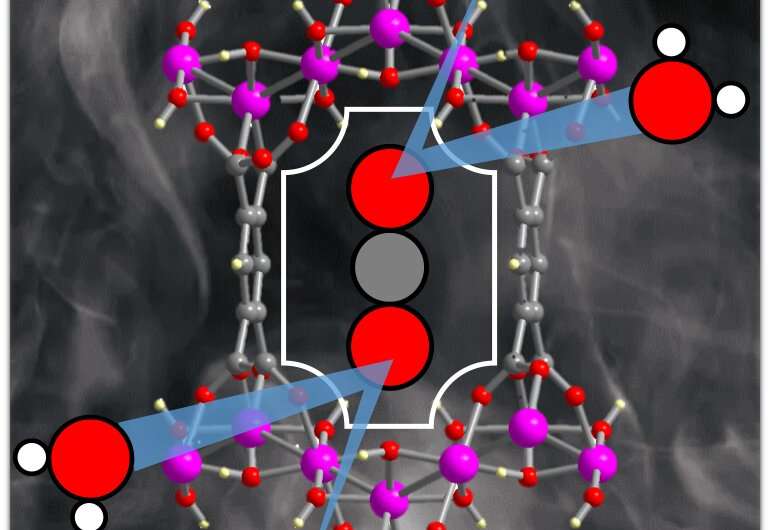
Scientists find a better way to capture carbon from industrial emissions (13/07/2023)
Researchers in the Oregon State University College of
Science have demonstrated the potential of an inexpensive nanomaterial to scrub
carbon dioxide from industrial emissions.
This clever material made from fungi could save your home in a fire (12/07/2023)
Scientists often talk about fungi in ‘iceberg’ terms, in that what you see above the surface is a small fraction of what lies beneath. Dig into the dirt below a mushroom cup and you’re likely to find a vast network of mycelium, the nutrients and communications system that plays such an important role in ecosystem support.









