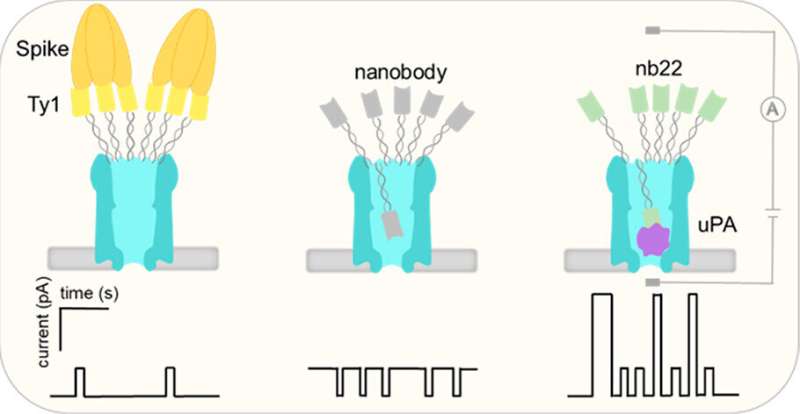
Tiny nanopores can contribute to faster identification of diseases (16/06/2023)
In a collaboration with Groningen
University, Professor Jørgen Kjems and his research group at Aarhus University
have achieved a remarkable breakthrough in developing tiny nano-sized pores
that can contribute to better possibilities for, among other things, detecting
diseases at an earlier stage.

Physicists design metamaterials with built-in frustration for mechanical memory (15/06/2023)
Researchers from the UvA
Institute of Physics and ENS de Lyon have discovered how to design materials
that necessarily have a point or line where the material doesn't deform under
stress, and that even remember how they have been poked or squeezed in the
past. These results could be used in robotics and mechanical computers, while
similar design principles could be used in quantum computers.
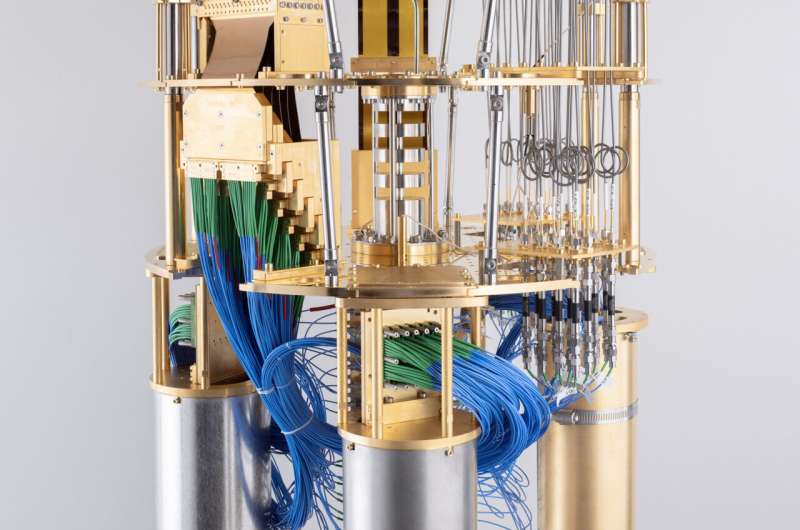

New technique in error-prone quantum computing makes classical computers sweat (15/06/2023)
Despite steady improvements in
quantum computers, they're still noisy and error-prone, which leads to
questionable or wrong answers. Scientists predict that they won't truly
outcompete today's "classical" supercomputers for at least five or
ten years, until researchers can adequately correct the errors that bedevil
entangled quantum bits, or qubits.
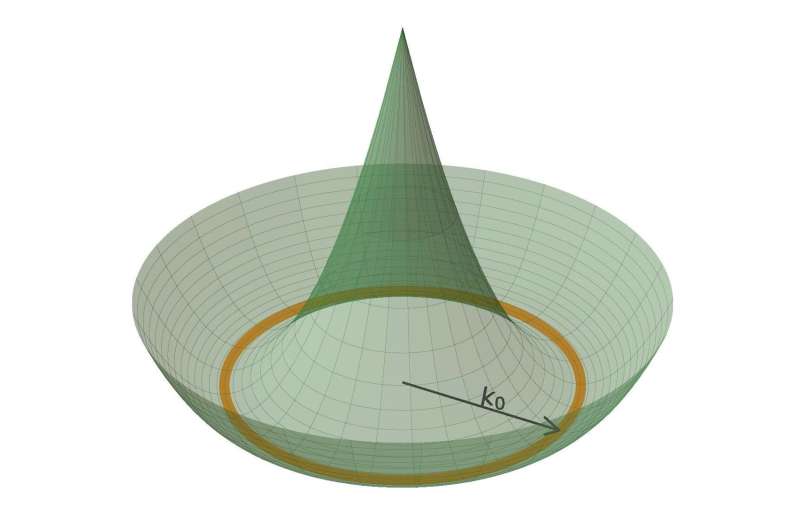
For experimental physicists, quantum frustration leads to fundamental discovery (15/06/2023)
A team of physicists, including
University of Massachusetts assistant professor Tigran Sedrakyan, recently
announced in the journal Nature that they have discovered a new phase
of matter. Called the "chiral Bose-liquid state," the discovery opens
a new path in the age-old effort to understand the nature of the physical
world.
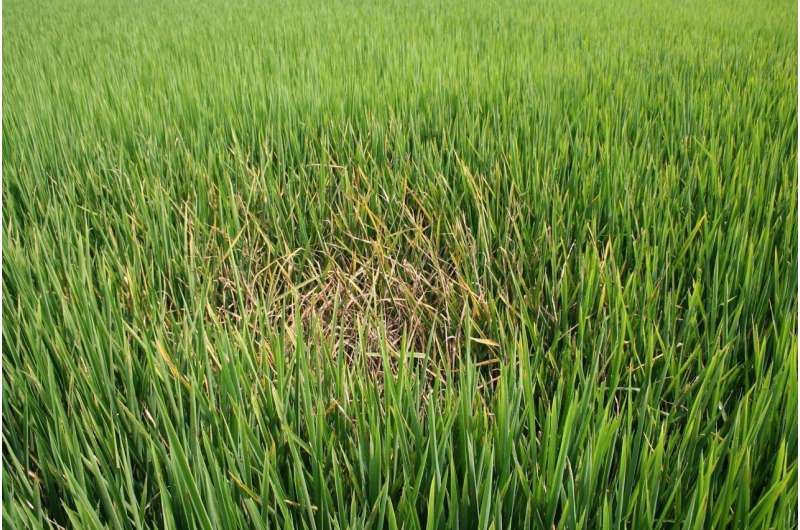

Genome editing used to create disease-resistant rice (15/06/2023)
Researchers from the University of California, Davis, and an international team of scientists have used the genome-editing tool CRISPR-Cas to create disease-resistant rice plants, according to a new study published in the journal Nature June 14.
Researchers provide comprehensive review of quantum teleportation (14/06/2023)
A team led by Prof. Guo Guangcan
from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) provides a comprehensive overview of
the progress achieved in the field of quantum teleportation. The team, which
includes Prof. Hu Xiaomin, Prof. Guo Yu, Prof. Liu Biheng, and Prof. Li
Chuanfeng from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), CAS,
was invited to publish a review paper on quantum teleportation in Nature
Review Physics.
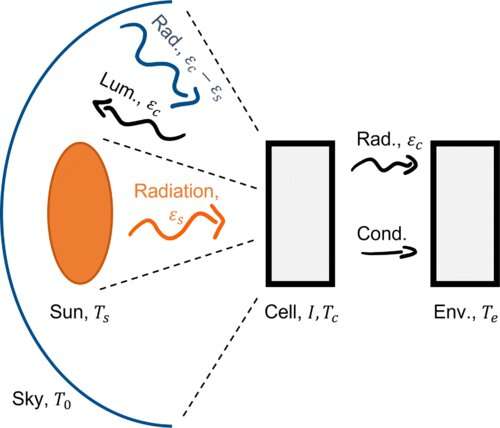
New approach for understanding temperature effects on photovoltaic device performance (14/06/2023)
Photovoltaic technology is
indispensable for our ability to mitigate climate change. Nonetheless, more
than 70% of the energy made available to us by the sun is wasted in
conventional photovoltaic cells. There is little hope for sustainable
technological advancement without addressing this issue.
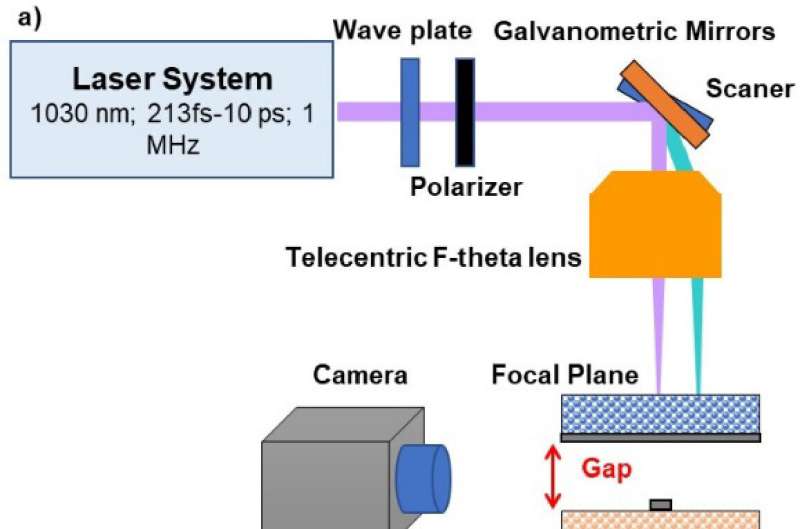
Researchers achieve first-ever printing of materials using laser techniques that change with voltage (14/06/2023)
Researchers from the Holography
and Optical Processing Group (GHPO) have succeeded in printing tunable
materials for the first time using high-precision laser techniques. This
development has been published in the journal Optics Express and
demonstrates that it is possible to print a polymer doped with liquid crystal,
which opens the door to using this fast, high-precision and environmentally
friendly technique in the manufacture of tunable devices.
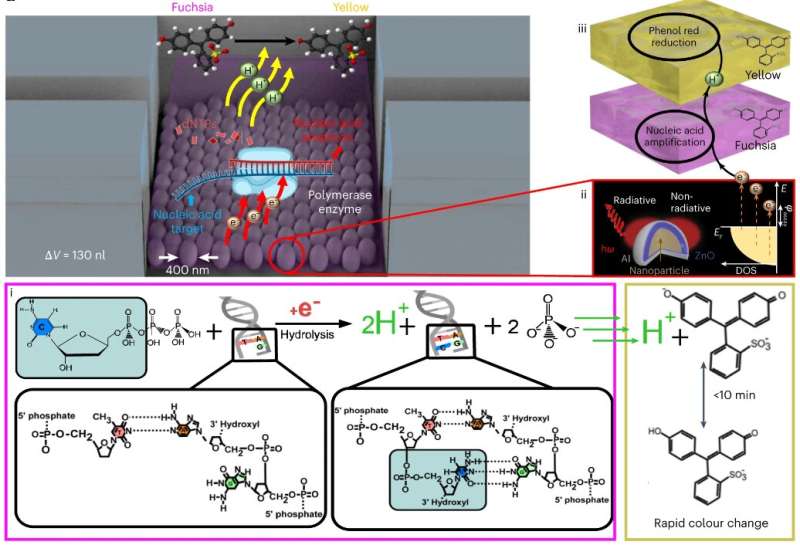
New diagnostic platform uses nanotechnology and machine learning to identify infectious diseases quickly (13/06/2023)
Infectious diseases and
respiratory infections in particular are a leading cause of global mortality.
As such, there is an urgent need for rapid, large-scale diagnostic tools that
can detect these diseases early, something which doesn't currently exist. To
address these problems, McGill University Professor of Bioengineering Sara
Mahshid's lab has developed an all-in-one detection platform (QolorEX) that can
deliver test results in just 13 minutes.
Light-activated concrete scrubs air pollution out of traffic tunnels (06/06/2023)









