
Scientific advances can make it easier to recycle plastics (18/11/2017)
Most of the 150 million tons of plastics produced around the world every year end up in landfills, the oceans and elsewhere. Less than 9 percent of plastics are recycled in the United States, rising to about 30 percent in Europe.

Pine and poplar wood improve sunlight-driven water purification (16/11/2017)
Engineers at the University of Maryland have found that porous types of wood from trees like poplar and pine can greatly increase the efficiency of water-to-steam conversion under sunlight. The findings, published November 15 in the journal Joule, could be used in a simple and inexpensive biodegradable device for water purification.

How extreme shocks deform a metal’s atomic structure (16/11/2017)
A new way to observe this deformation as it happens can help study a wide range of phenomena, from meteor impacts to high-performance ceramics used in armor, as well as how to protect spacecraft from high-speed dust impacts.
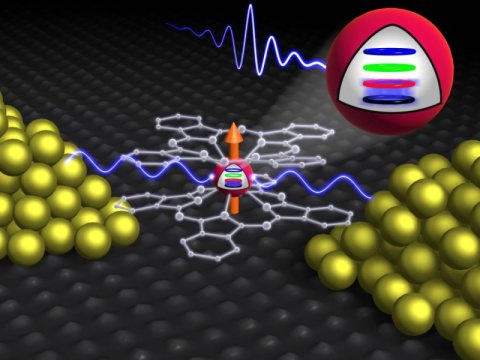
Quantum computing with molecules for a quicker search of unsorted databases (16/11/2017)
Scrapbooks or social networks are collections of mostly unsorted data. The search for single elements in very large data volumes, i.e. for the needle in the data haystack, is extremely complex for classical computers. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now quantum mechanically implemented and successfully executed Grover's algorithm, a process for the quick finding of a search element in unsorted databases.

Ionic 'solar cell' could provide on-demand water desalination (16/11/2017)
Modern solar cells, which use energy from light to generate electrons and holes that are then transported out of semiconducting materials, have existed for over 60 years. Little attention has been paid, however, to the promise of using light to drive the transport of oppositely charged protons and hydroxides obtained by dissociating water molecules. Researchers report such a design, which has promising application in producing electricity to turn brackish water drinkable.

Researchers take next step toward fusion energy (15/11/2017)
Fusion is the process that powers the sun, harnessing it on Earth would provide unlimited clean energy. However, researchers say that constructing a fusion power plant has proven to be a daunting task, in no small part because there have been no materials that could survive the grueling conditions found in the core of a fusion reactor. Now, researchers at Texas A&M University have discovered a way to make materials that may be suitable for use in future fusion reactors.

Breakthrough research suggests potential treatment for autism, intellectual disability (15/11/2017)
A breakthrough in finding the mechanism and a possible therapeutic fix for autism and intellectual disability has been made by a University of Nebraska Medical Center researcher and his team at the Munroe-Meyer Institute (MMI).

Exercise maintains brain size, new research finds (14/11/2017)
Aerobic exercise can improve memory function and maintain brain health as we age, a new Australian-led study has found.

New technology makes artificial intelligence more private and portable (14/11/2017)
Technology developed at the University of Waterloo is paving the way for artificial intelligence (AI) to break free of the internet and cloud computing.
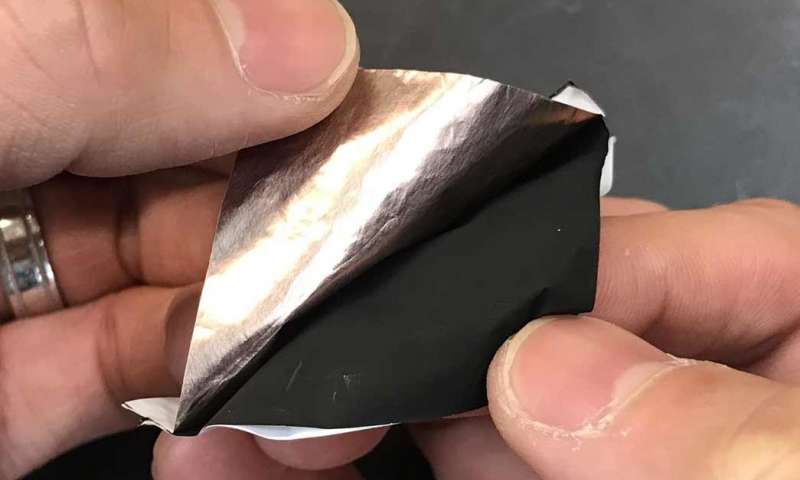

Clothing made from a reversible fabric could warm or cool wearers and keep them comfortable (14/11/2017)
Stanford researchers have developed a reversible fabric that, without expending effort or energy, keeps skin a comfortable temperature whatever the weather.









