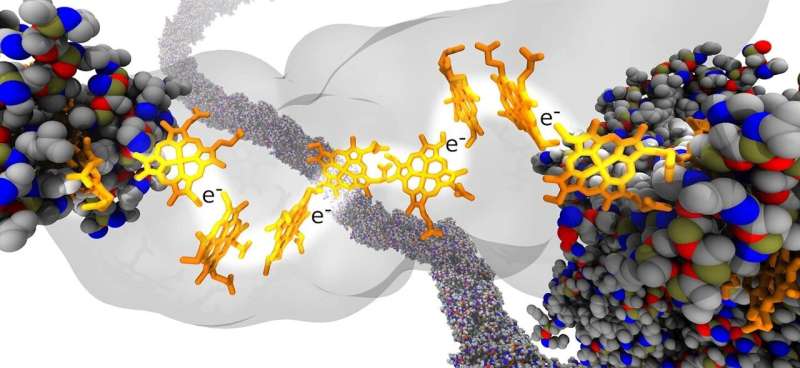
Simulating how electrons move through biological nanowires (13/11/2023)
The movement of electrons across
wires is what allows us to use electricity every day. Biological nanowires,
microscopic wires made of proteins, have caught researchers' attention for
their ability to carry electrons over long distances.
Sun-run device turns dirty water into hydrogen fuel & drinking water (13/11/2023)
Ultra-white ceramic cools buildings with record-high 99.6% reflectivity (12/11/2023)
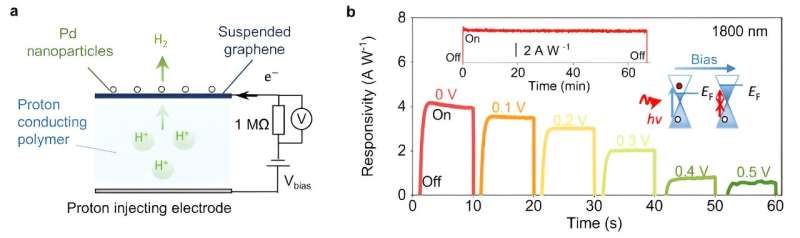
Graphene's proton permeability: A switch for future energy technologies (08/11/2023)
Researchers from the National
Graphene Institute at the University of Manchester have discovered a way to use
light to accelerate proton transport through graphene, which could
revolutionize the way we generate hydrogen.
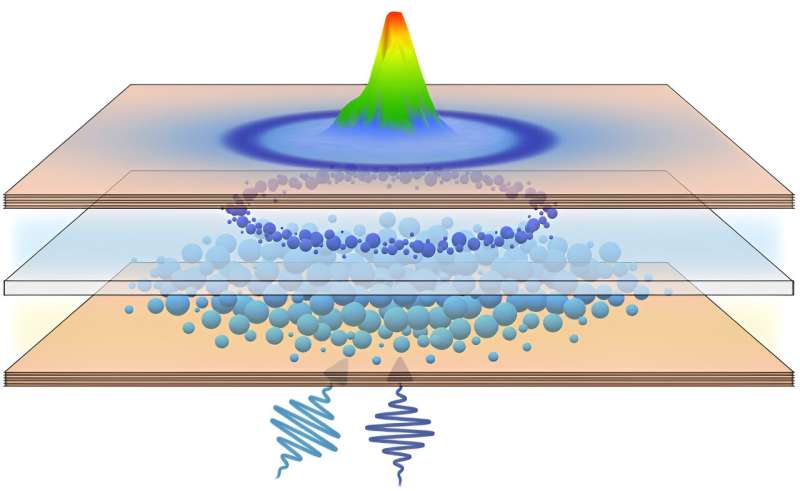
Scientists manipulate quantum fluids of light, bringing us closer to next-generation unconventional computing (07/11/2023)
In a quantum leap toward the
future of unconventional computing technologies, a team of physicists made an
advancement in spatial manipulation and energy control of room-temperature
quantum fluids of light, aka polariton condensates, marking a pivotal milestone
for the development of high-speed, all-optical polariton logic devices that
have long held the key to next-generation unconventional computing, according
to a recently published paper in Physical Review Letters.
Impressive new plastic self-heals, can be recycled and feeds marine life (05/11/2023)
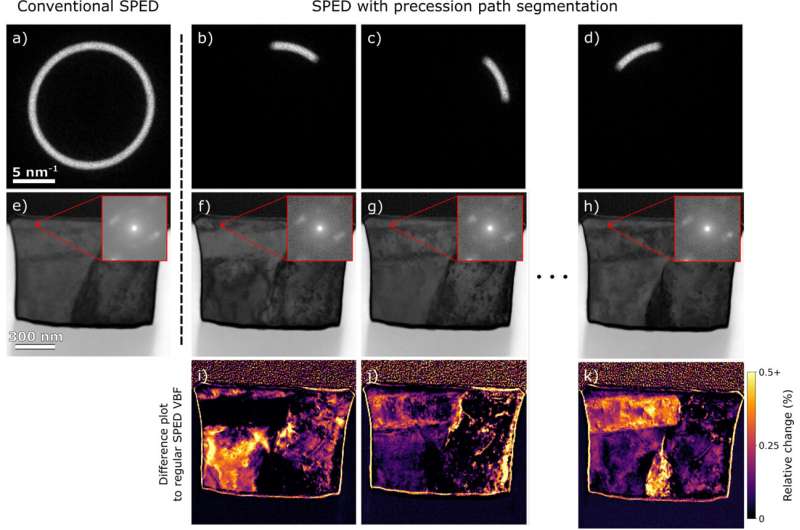
Solving a long-standing problem in transmission electron microscopy (04/11/2023)
For researchers wanting to
understand the inner workings of magnetic materials, transmission electron
microscopy is an indispensable tool. Because the wavelength of an electron is
much shorter than the wavelength of visible light, a beam of electrons transmitted
through a thin slice of a material can create an image in which the inner
structure of the material is magnified up to 50 million times, many orders of
magnitude more than with an optical microscope.
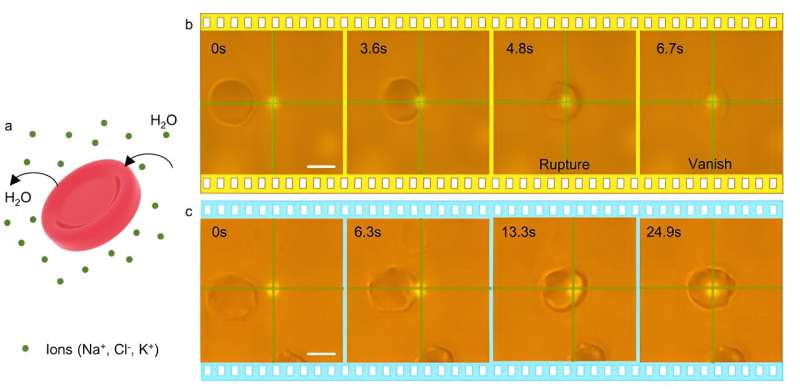
Scientists use supercomputers to make optical tweezers safer for living cells (03/11/2023)
Optical tweezers manipulate tiny
things like cells and nanoparticles using lasers. While they might sound like
tractor beams from science fiction, the fact is their development garnered scientists
a Nobel Prize in 2018.
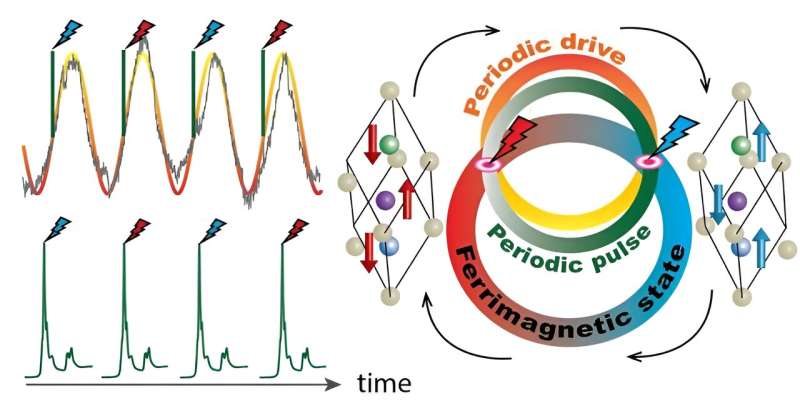
Strange magnetic material could make computing energy-efficient (02/11/2023)
A research collaboration co-led
by EPFL has uncovered a surprising magnetic property of an exotic material that
might lead to computers that need less than one-millionth of the energy
required to switch a single bit.
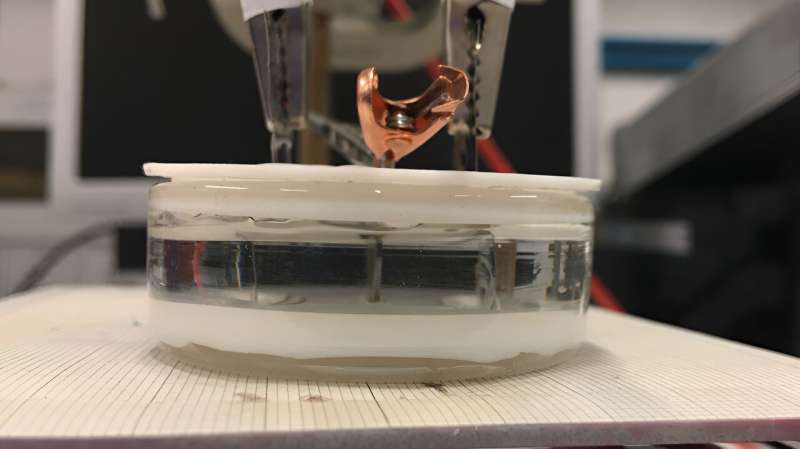
First-ever wireless device developed to make magnetism appear in non-magnetic materials (02/11/2023)
Researchers at the UAB and ICMAB
have succeeded in bringing wireless technology to the fundamental level of
magnetic devices. The emergence and control of magnetic properties in cobalt
nitride layers (initially non-magnetic) by voltage, without connecting the
sample to electrical wiring, represents a paradigm shift that can facilitate
the creation of magnetic nanorobots for biomedicine and computing systems where
basic information management processes do not require wiring.









