Great Pyramid tombs unearth "proof" workers were not slaves (14/01/2010)
The tombs contained no gold or valuables, which safeguarded them from tomb raiders throughout antiquity, and the bodies were not mummified. The skeletons were found buried in a foetal position – the head pointing to the west and the feet to the east according to ancient Egyptian beliefs, surrounded by jars once filled with supplies for afterlife. Egypt"s leading archaeologist says 4,000-year-old burial plots with skeletons expose myth that builders were slaves.
Egypt"s leading archaeologist says 4,000-year-old burial plots with skeletons expose myth that builders were slaves.
Few Gender Differences in Math Abilities, Worldwide Study Finds (08/01/2010)
 Girls around the world are not worse at math than boys, even though boys are more confident in their math abilities, and girls from countries where gender equity is more prevalent are more likely to perform better on mathematics assessment tests, according to a new analysis of international research.
Girls around the world are not worse at math than boys, even though boys are more confident in their math abilities, and girls from countries where gender equity is more prevalent are more likely to perform better on mathematics assessment tests, according to a new analysis of international research.
Five New Exoplanets Discovered By NASA's Kepler Space Telescope (06/01/2010)
 NASA's Kepler space telescope, designed to find Earth-size planets in the habitable zone of sun-like stars, has discovered its first five new exoplanets, or planets beyond our solar system.
NASA's Kepler space telescope, designed to find Earth-size planets in the habitable zone of sun-like stars, has discovered its first five new exoplanets, or planets beyond our solar system.
Kepler's high sensitivity to both small and large planets enabled the discovery of the exoplanets, named Kepler 4b, 5b, 6b, 7b and 8b. The discoveries were announced Monday, Jan. 4, by members of the Kepler science team during a news briefing at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Washington.
Psychologists Show That Future-Minded People Make Better Decisions for Their Health (25/12/2009)
When New Year"s Eve rolls around and you are deciding whether to have another glass of champagne, your decision may be predicted by your perspective of the future.
Human Protein Helps Prevent Infection by H1N1 Influenza and Other Viruses (19/12/2009)
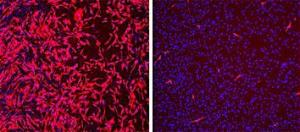 Howard Hughes Medical Institute researchers have identified a naturally occurring human protein that helps prevent infection by H1N1 influenza and other viruses, including West Nile and dengue virus.
Howard Hughes Medical Institute researchers have identified a naturally occurring human protein that helps prevent infection by H1N1 influenza and other viruses, including West Nile and dengue virus.
Nanosensors Used to Measure Cancer Biomarkers in Blood for First Time (15/12/2009)
 A team led by
A team led by
VN’s mathematician in top ten scientific discoveries for Time Magazine (12/12/2009)
1. Our Oldest Ancestor, "Ardi" 2. The Human Epigenome, Decoded 3. Gene Therapy Cures Color Blindness 7. The Fundamental Lemma, Solved  Time Magazine on December 9 announced its top ten lists for 2009, and includes Vietnamese Professor Ngo Bao Chau"s solving of the “fundamental lemma”.
Time Magazine on December 9 announced its top ten lists for 2009, and includes Vietnamese Professor Ngo Bao Chau"s solving of the “fundamental lemma”.
Top 10 Scientific Discoveries:
Snowflake Chemistry Could Give Clues About Ozone Depletion (10/12/2009)
 The structure of the frosty flakes also fascinate ice chemists like Purdue University"s Travis Knepp, a doctoral candidate in analytical chemistry who studies the basics of snowflake structure to gain more insight into the dynamics of ground-level, or "tropospheric," ozone depletion in the Arctic.
The structure of the frosty flakes also fascinate ice chemists like Purdue University"s Travis Knepp, a doctoral candidate in analytical chemistry who studies the basics of snowflake structure to gain more insight into the dynamics of ground-level, or "tropospheric," ozone depletion in the Arctic.
Antarctica may heat up dramatically as ozone hole repairs, warn scientists (05/12/2009)
The hole in the Earth"s ozone layer has shielded Antarctica from the worst effects of global warming until now, according to the most comprehensive review to date of the state of the Antarctic climate. But scientists warned that as the hole closes up in the next few decades, temperatures on the continent could rise by around 3C on average, with melting ice contributing to a global sea-level increases of up to 1.4m. As blanket of ozone over southern pole seals up, temperatures on continent could soar by 3C, increasing sea level rise by 1.4m.
As blanket of ozone over southern pole seals up, temperatures on continent could soar by 3C, increasing sea level rise by 1.4m.
New Brain Connections Form Rapidly During Motor Learning (01/12/2009)
 New connections begin to form between brain cells almost immediately as animals learn a new task, according to a study published recently in Nature. Led by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, the study involved detailed observations of the rewiring processes that take place in the brain during motor learning.
New connections begin to form between brain cells almost immediately as animals learn a new task, according to a study published recently in Nature. Led by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, the study involved detailed observations of the rewiring processes that take place in the brain during motor learning.









