Emerging
contaminants (ECs) in natural water bodies, including endocrine disruptors,
pharmaceuticals, and synthetic dyes, pose a grave threat to public water
safety. Current wastewater treatment technologies, while somewhat effective,
fall short of efficiently removing these contaminants due to their hydrophobic
nature and low-level concentrations.
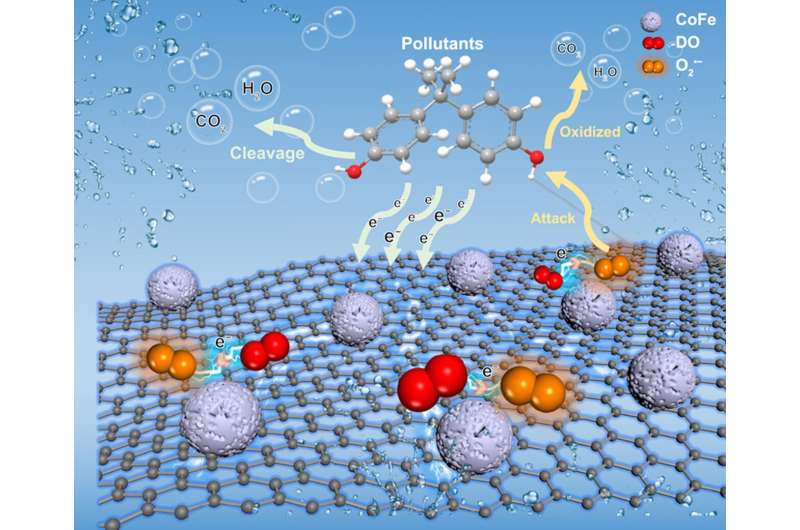
In a study published in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Guangzhou University introduced a CoFeQds@GN-Nws catalyst system that uniquely exploits the internal energy present in wastewater. The catalyst's surface features electron-rich and electron-poor micro-regions, fostering a self-purification mechanism.
This process not only cleaves and oxidizes pollutants but also activates dissolved oxygen into superoxide radical, enhancing pollutant removal. Remarkably, the system operates at ambient temperature and pressure without external oxidants, achieving near-total removal of ECs.
The study reveals the role of CoFe quantum dots in creating an unbalanced electron distribution, which is crucial for the catalyst's efficacy, driving the electron-donation effect of pollutants and the activation of dissolved oxygen into reactive oxygen species, an innovative purification process.
Professor Lai Lyu, the leading author of this research, stated, "The development of the CoFeQds@GN-Nws system marks a paradigm shift in wastewater treatment technologies. By leveraging the internal energy of wastewater and reducing dependence on external resources, this method not only addresses the challenge of ECs removal but also aligns with global sustainability goals."
The CoFeQds@GN-Nws system presents a transformative approach in water purification technology. By reducing the resource and energy demands of water treatment, the system contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to managing water pollution. This innovative technology aligns with global efforts towards carbon neutrality and emission reduction, reinforcing the commitment to sustainable water security solutions.

 Previous page
Previous page Back to top
Back to top







