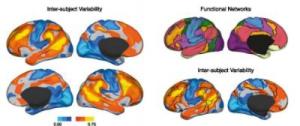
"Understanding the normal range of individual variability in the human brain will help us identify and potentially treat regions likely to form abnormal circuitry, as manifested in neuropsychiatric disorders," says senior author Dr. Hesheng Liu, of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Dr. Liu and his colleagues used an imaging technique called resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging to examine person-to-person variability of brain connectivity in 23 healthy individuals five times over the course of six months. The researchers discovered that the brain regions devoted to control and attention displayed a greater difference in connectivity across individuals than the regions dedicated to our senses like touch and sight. When they looked at other published studies, the investigators found that brain regions previously shown to relate to individual differences in cognition and behavior overlap with the regions identified in this study to have high variability among individuals. The researchers were therefore able to pinpoint the areas of the brain where variable connectivity causes people to think and behave differently from one another. Higher rates of variability across individuals were also displayed in regions of the brain that have undergone greater expansion during evolution. "Our findings have potential implications for understanding brain evolution and development," says Dr. Liu. "This study provides a possible linkage between the diversity of human abilities and evolutionary expansion of specific brain regions," he adds.

 Previous page
Previous page Back to top
Back to top







