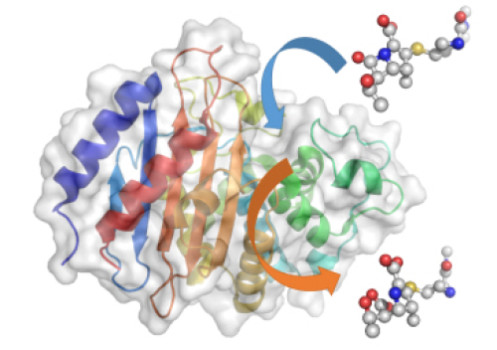
Researchers at the University of Bristol focused on the role of enzymes in the bacteria, which split the structure of the antibiotic and stop it working, making the bacteria resistant.
It's hoped this insight will help scientists to develop new antibiotics with a much lower risk of resistance, and to choose the best medicines for specific outbreaks.
Using a Nobel Prize-winning technique called QM/MM -- quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics simulations - the Bristol research team were able to gain a molecular-level insight into how enzymes called 'beta-lactamases' react to antibiotics.
Researchers specifically want to understand the growing resistance to carbapenems, which are known as the 'last resort' antibiotics for many bacterial infections and super bugs such as E. coli.
Resistance to carbapenems makes some bacterial infections untreatable, resulting in minor infections becoming very dangerous and potentially deadly.
The QM/MM simulations revealed that the most important step in the whole process is when the enzyme 'spits out' the broken down antibiotic. If this happens quickly, then the enzyme is able to go on chewing up antibiotics and the bacterium is resistant. If it happens slowly, then the enzyme gets 'clogged up' and can't break down any more antibiotics, so the bacterium is more likely to die.
The rate of this 'spitting out' depends on the height of the energy barrier for the reaction -- if the barrier is high, it happens slowly; if it's low, it happens much more quickly.
Professor Adrian Mulholland, from Bristol University's School of Chemistry, said: "We've shown that we can use computer simulations to identify which enzymes break down and spit out carbapenems quickly and those that do it only slowly.

 Previous page
Previous page Back to top
Back to top







