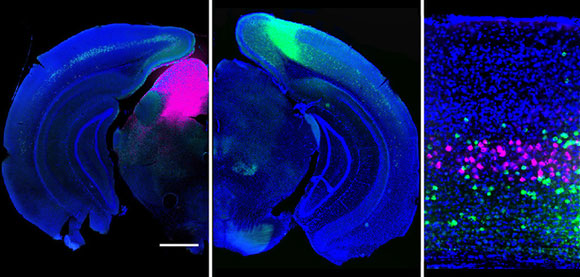
Newly published research from Yale’s Department of Neuroscience provides some clues to how cells in the visual cortex direct sensory information to different targets throughout the brain.
“These results demonstrate how the brain processes multiple sensory inputs in parallel,” Higley said, noting that the findings help reveal the normal flow of information in the brain, opening new avenues for understanding how perturbations of these systems might contribute to abnormal behavior.

 Previous page
Previous page Back to top
Back to top







