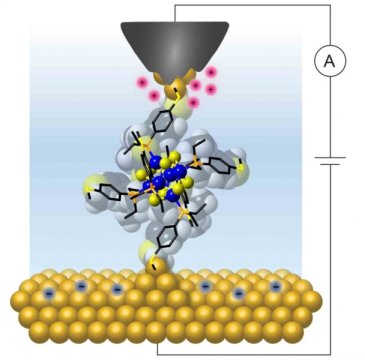
Single molecules can work as reproducible transistors -- at room temperature (19/08/2017)
Researchers have now reproducibly demonstrated current
blockade -- the ability to switch a device from the insulating to the
conducting state where charge is added and removed one electron at a time --
using atomically precise molecular clusters at room temperature. The study
shows that single molecules can function as reproducible circuit elements such
as transistors or diodes that can easily operate at room temperature.

Tough, self-healing rubber developed (17/08/2017)
Imagine a tire that
could heal after being punctured or a rubber band that never snapped.
Researchers have developed a new type of rubber that is as tough as natural
rubber but can also self-heal.

Adapters enable better communication between machines (03/08/2017)
Plug and play is a
technology that allows users to connect devices such as printers or USB memory
sticks to a computer and directly use them without installing any software.
This technology is now also available for industrial applications: Engineers
developed an adapter that makes it much easier to interconnect parts of a
production facility and align them with each other.
New 3-D technique uses water and robotics to reconstruct complex objects (03/08/2017)
An international group of researchers developed a
technique that results in more accurate 3-D scanning for reconstructing complex
objects than what currently exists. The innovative method combines robotics and
water.

New material resembling a metal nanosponge could reduce computer energy consumption (03/08/2017)
A nanoporous material
has been developed based on a copper and nickel alloy, with a structure similar
to that of a sponge with pores measuring the size of a millionth of a
millimeter, which allows handling and storing information using very little
energy. These nanosponges could be the base of new magnetic memories for
computers and mobile phones with greater energy efficiency than those currently
existing.

Single-photon emitter has promise for quantum info-processing (03/08/2017)
Los Alamos National Laboratory has produced the first
known material capable of single-photon emission at room temperature and at
telecommunications wavelengths. These carbon nanotube quantum light emitters
may be important for optically-based quantum information processing and
information security, while also being of significant interest for
ultrasensitive sensing, metrology and imaging needs and as photon sources for
fundamental advances in quantum optics studies. The research was reported today
in the journal Nature Photonics.

Ultracold molecules hold promise for quantum computing (03/08/2017)
A study by MIT
researchers shows that collections of ultracold molecules can retain the
information stored in them for hundreds of times longer than previously
achieved in these materials. These clusters might thus serve as 'qubits,' the
basic building blocks of quantum computers.
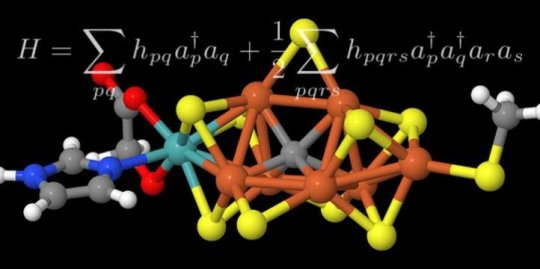
Clarifiying complex chemical processes with quantum computers (03/08/2017)
Science and the IT
industry have high hopes for quantum computing, but descriptions of possible
applications tend to be vague. Researchers have now come up with a concrete
example that demonstrates what quantum computers will actually be able to
achieve in the future.

Artificial intelligence helps build brain atlas of fly behavior (01/08/2017)
Scientists have created comprehensive brain maps linking
different groups of neurons to specific behaviors, using a machine-learning
program that annotated more than 225 days of videos of flies -- a feat that
would have taken humans some 3,800 years.

Living computers: RNA circuits transform cells into nanodevices (01/08/2017)
Scientists have
demonstrated how living cells can be induced to carry out computations in the
manner of tiny robots or computers.









