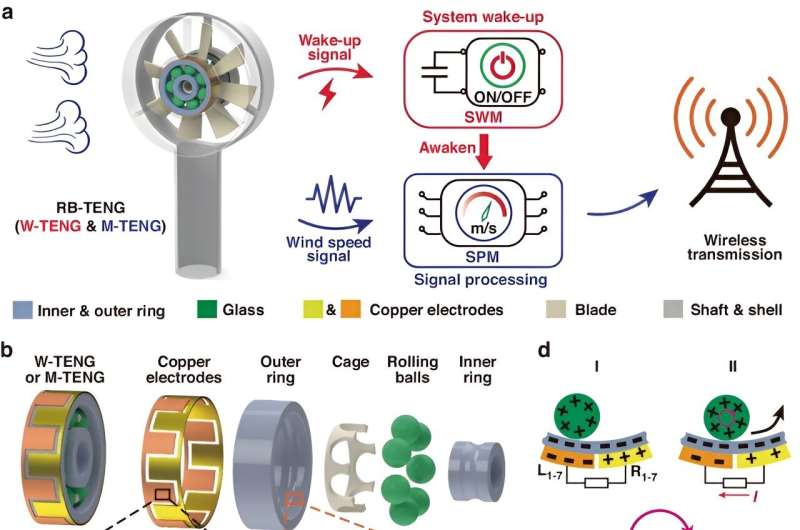
New wind speed sensor uses minimal power for advanced weather tracking (05/06/2024)
Researchers
have unveiled a pioneering breeze wake-up anemometer (B-WA), employing a
rolling-bearing triboelectric nanogenerator (RB-TENG) that provides a new
strategy for low-energy consumption environmental monitoring. The ability of
the B-WA to operate autonomously and efficiently in varying wind conditions
marks a substantial advancement in the field of sustainable environmental
monitoring.

Microsoft’s Power Platform updates hint at the future of enterprise coding (23/05/2024)
Copilot-powered security tools, simplified developer collaboration, and easier integration of voice-activated generative AI into mobile apps are among the changes on show at Build.
Scientists say they’ve found where the sun’s magnetic field originates (23/05/2024)
The sun has a powerful magnetic field that
creates sunspots on the star’s surface and unleashes solar storms such as the
one that bathed much of the planet in beautiful auroras this month.
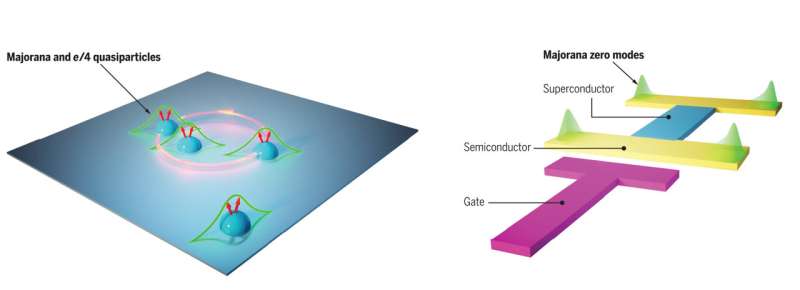
Quantum experts review major techniques for isolating Majoranas (19/05/2024)
Named after an Italian
theoretical physicist, Majoranas are complex quasiparticles that could be the
key to building next-generation quantum computing systems.
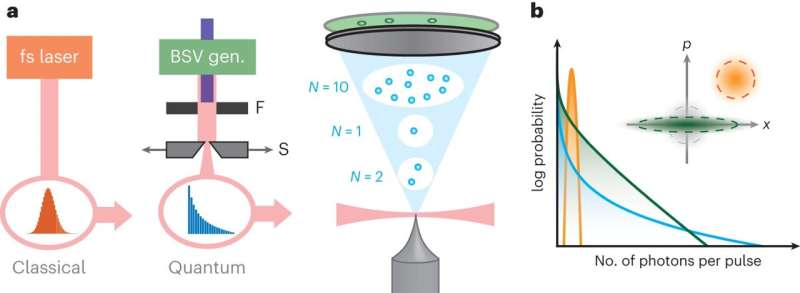
Researchers realize multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light (19/05/2024)
Strong field quantum optics is a
rapidly emerging research topic, which merges elements of non-linear
photoemission rooted in strong field physics with the well-established realm of
quantum optics. While the distribution of light particles (i.e., photons) has
been widely documented both in classical and non-classical light sources, the
impact of such distributions on photoemission processes remains poorly
understood.
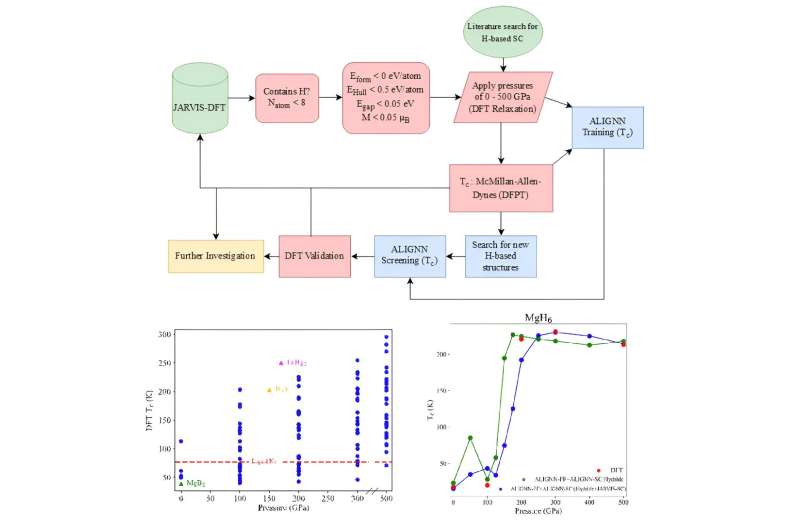
Coupling quantum mechanical simulations and AI paves way for screening new superconductors (19/05/2024)
Superconductors are materials
that conduct electricity without resistance and are essential for several
technological advancements, which include medical imaging and energy-efficient
technology. However, most known superconductors operate under extreme conditions
such as extremely low temperatures or high pressures, which limit their
practical use.
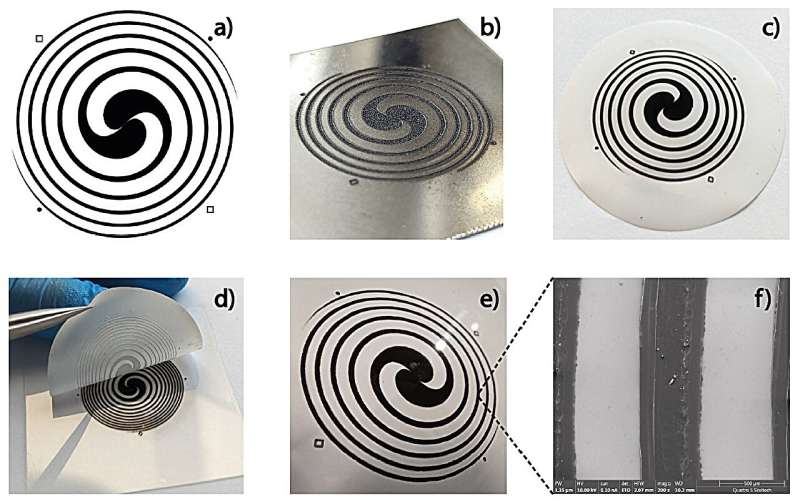
Physicists create optical component for 6G (18/05/2024)
A joint team of physicists from
Skoltech, MIPT, and ITMO developed an optical component that helps manage the
properties of a terahertz beam and split it into several channels. The new
device can be used as a modulator and generator of terahertz vortex beams in
medicine, 6G communications, and microscopy. The paper appears in the
journal Advanced Optical Materials.
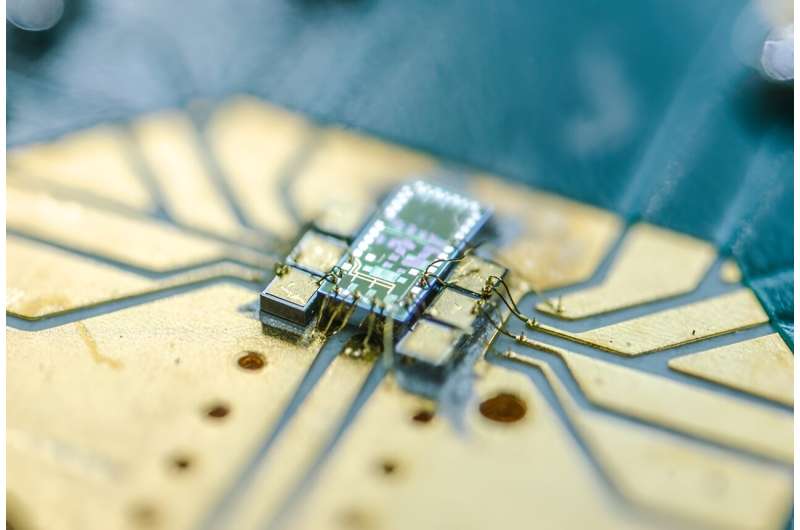
Researchers develop world's smallest quantum light detector on a silicon chip (18/05/2024)
Researchers at the University of
Bristol have made an important breakthrough in scaling quantum technology by
integrating the world's tiniest quantum light detector onto a silicon chip. The
paper, "A Bi-CMOS electronic photonic integrated circuit quantum light
detector," was published in Science Advances.
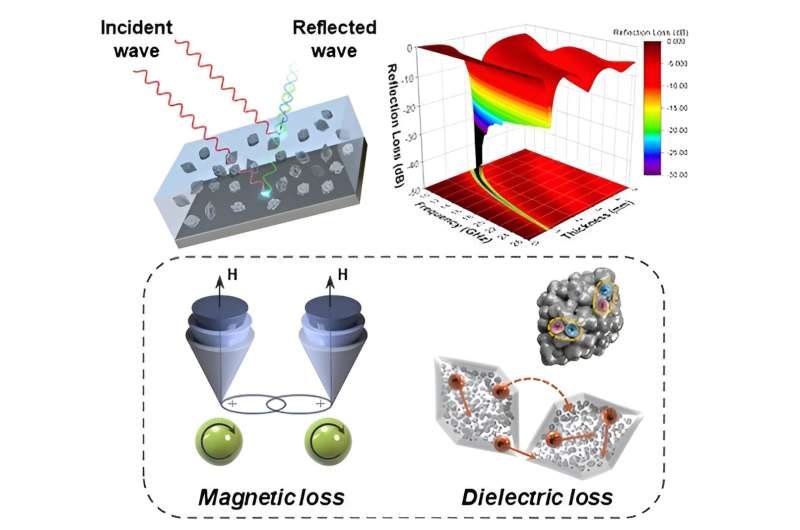
Research team develops electromagnetic wave absorbers with strong absorption and broad effective bandwidth (17/05/2024)
A research team from the
Department of Functional Composites in Composites Research Division at Korea
Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) has successfully developed
electromagnetic wave absorbers based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that
enhance dielectric and magnetic losses in the gigahertz (GHz) frequency band.
The research was published in the journal Advanced Composites
and Hybrid Materials on February 5, 2024.
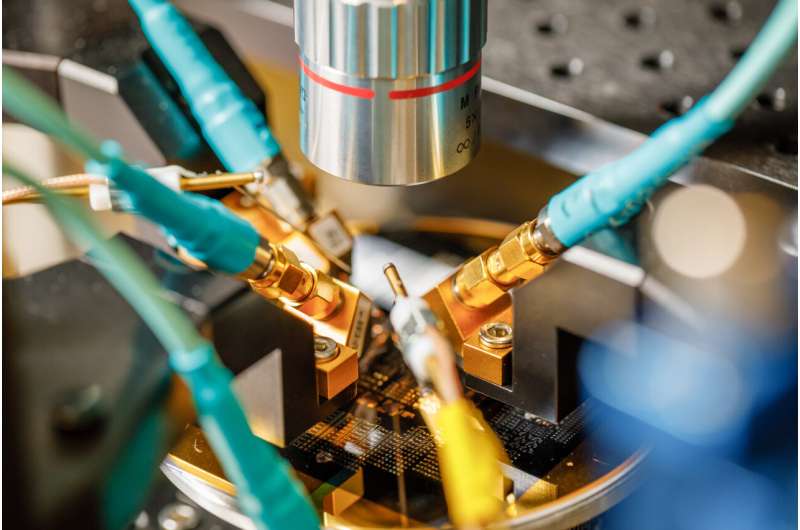

New phononics materials may lead to smaller, more powerful wireless devices (12/05/2024)
What if your earbuds could do
everything your smartphone can do already, except better? What sounds a bit
like science fiction may actually not be so far off. A new class of synthetic
materials could herald the next revolution of wireless technologies, enabling
devices to be smaller, require less signal strength and use less power.









