Clever armadillo-inspired "fabric" gets stiff or soft as needed (23/07/2024)
Soft materials and stiff materials both have their uses, but
the two properties typically aren't seen in one substance. RoboFabric is an
exception, then, in that it can be switched back and forth between soft and
stiff states.
New method achieves controllable tuning, assesses instability in 2D materials for engineering applications (22/07/2024)
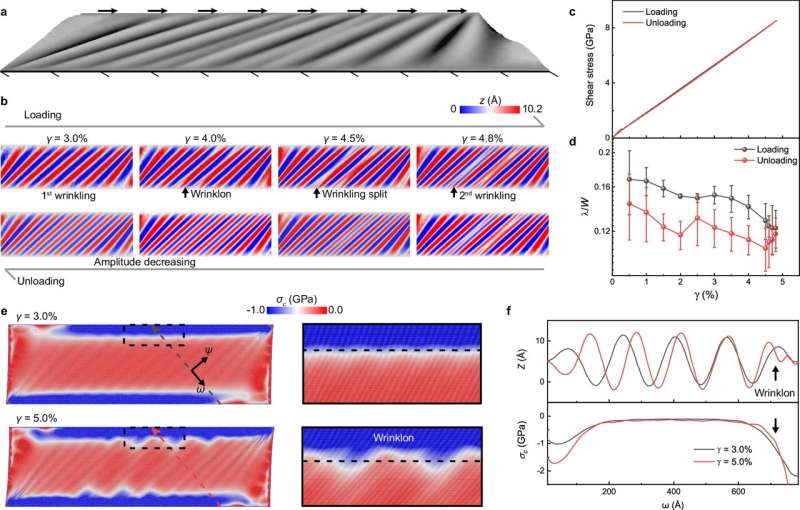
Two-dimensional (2D) materials
have atomic-level thickness and excellent mechanical and physical properties,
with broad application prospects in fields such as semiconductors, flexible
devices, and composite materials.
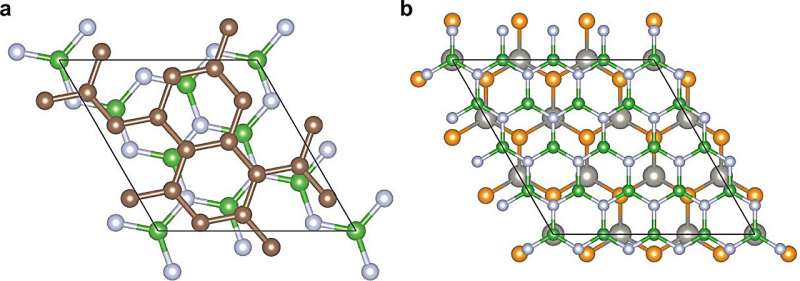
Atomically thin transducers could one day enable quantum computing at room temperature (22/07/2024)
Quantum computers have to be kept
cold to function—very cold. These machines generally run at "just a few
degrees above absolute zero," says Yoseob Yoon, assistant professor of
mechanical and industrial engineering at Northeastern University. "It's
colder than outer space."
Researchers achieve unprecedented nanostructuring inside silicon (22/07/2024)
Silicon, the cornerstone of
modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, has traditionally been
limited to surface-level nanofabrication due to the challenges posed by
existing lithographic techniques. Available methods either fail to penetrate
the wafer surface without causing alterations or are limited by the
micron-scale resolution of laser lithography within Si.
Complete recycle of solid-state batteries possible, thanks to polymer layers (21/07/2024)
The recycled battery retained over 92 percent of the
original coin cell battery’s discharge capacity.
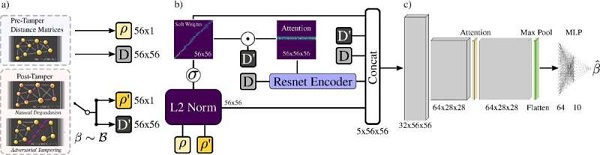
AI-powered optical detection to thwart counterfeit chips (20/07/2024)
The semiconductor industry has grown into a $500 billion
global market over the last 60 years. However, it is grappling with dual
challenges: a profound shortage of new chips and a surge of counterfeit chips,
introducing substantial risks of malfunction and unwanted surveillance.
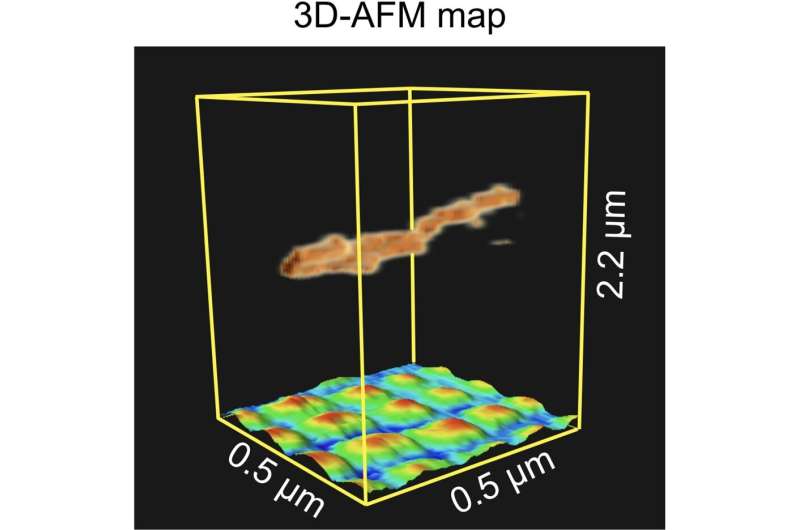
Researchers explain the imaging mechanisms of atomic force microscopy in 3D (19/07/2024)
Researchers at Nano Life Science
Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University report the 3D imaging of a
suspended nanostructure. The technique used is an extension of atomic force
microscopy and is a promising approach for visualizing various 3D biological
systems.
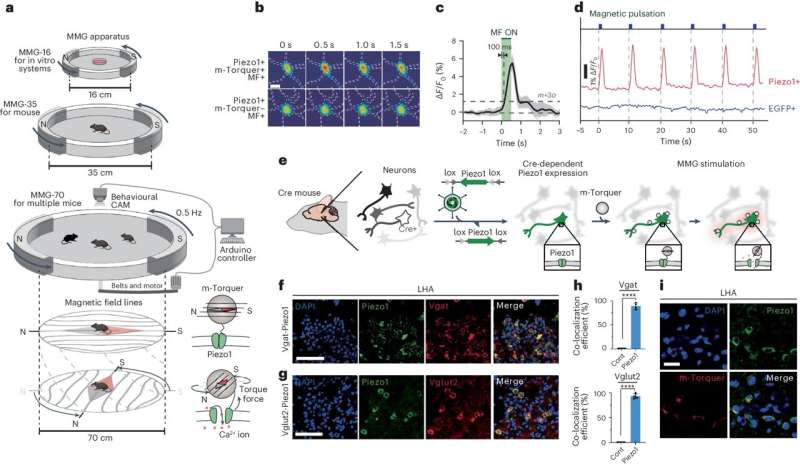
Nanomedicine researchers develop new technology to control neural circuits using magnetic fields (18/07/2024)
Researchers at the Center for
Nanomedicine within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and Yonsei University
in South Korea have unveiled a technology that can manipulate specific regions
of the brain using magnetic fields, potentially unlocking the secrets of
high-level brain functions such as cognition, emotion, and motivation.
Quantum microscopy study makes electrons visible in slow motion (16/07/2024)
Physicists at the University of Stuttgart under the
leadership of Prof. Sebastian Loth are developing quantum microscopy which
enables them for the first time to record the movement of electrons at the
atomic level with both extremely high spatial and temporal resolution.
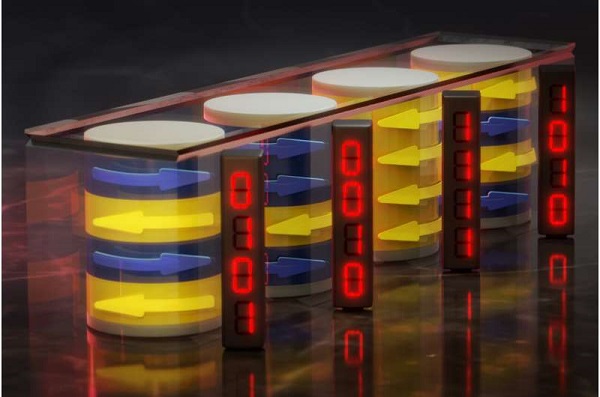
Metamaterials for the data highway: New concept offers potential for more efficient data storage (16/07/2024)
Researchers from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf
(HZDR), TU Chemnitz, TU Dresden and Forschungszentrum Jülich have been the
first to demonstrate that not just individual bits, but entire bit sequences
can be stored in cylindrical domains: tiny, cylindrical areas measuring just
around 100 nanometers.









