'Superlubricious' coating radically drops friction between metal parts (16/07/2024)
Using biowaste from cassava plants, scientists have created
a coating that virtually eliminates friction in metal parts. The breakthrough
has the potential to deliver better fuel economy, extend the lifespan of moving
parts, and deliver enormous savings in myriad industries.
New hybrid perovskite solar cell boasts long life and high efficiency (07/07/2024)
In the world of solar cell technology, perovskite materials
are poised to take on the current reigning champion silicon, but their
stability is holding them back. Now, scientists in China have developed a new
type of hybrid perovskite that boasts a very good efficiency over a long life.
New "glassy gel" materials are strangely strong, stretchy and sticky (01/07/2024)
Gels and glasses are on opposite ends of the material
spectrum, but engineers at North Carolina State University (NCSU) have
developed a new class called “glassy gels” that are both strong and flexible,
as well as sticky and self-healing.
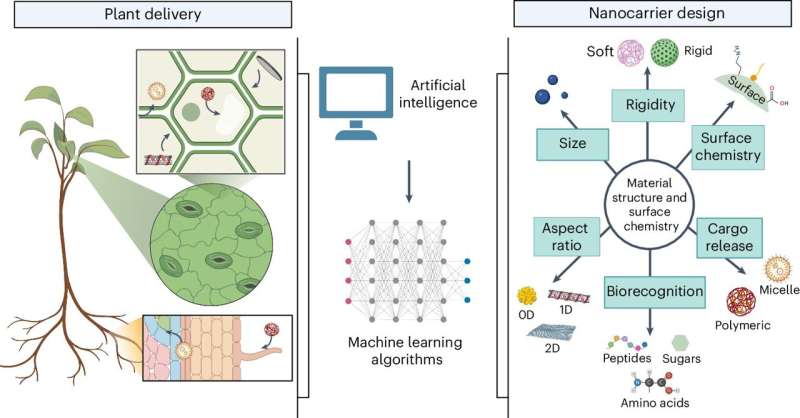
Better farming through nanotechnology: An argument for applying medical insights to agriculture (07/06/2024)
Advanced
technologies enable the controlled release of medicine to specific cells in the
body. Scientists argue these same technologies must be applied to agriculture
if growers are to meet increasing global food demands.
New tech could give individuals increased control over their own exposure to harmful gases (07/06/2024)
In an increasingly
health-conscious society, data is a hot commodity. Tracking step counts with an
old-school pedometer has turned into monitoring heart rates, sleep cycles and
blood oxygen levels with wearable fitness trackers, a market that has exploded
in recent years. But one critical aspect of health monitoring has yet to become
mainstream, because continuous air quality data is currently tied to spaces and
not people.
Laser-based 3D printing: A powerful tool to advance optical microscopy (07/06/2024)
Today, optical microscopy is one
of the most widely used methods in various multidisciplinary fields for
inspecting objects, organisms, or surfaces on a small scale. However, its
lateral resolution is fundamentally limited by the diffraction of light—a constraint
that, with the use of conventional lenses, has become increasingly critical as
the demand for higher resolutions grows.
Scientists create world's strongest iron-based superconducting magnet using AI (07/06/2024)
Scientists have developed the
world's strongest iron-based superconducting magnet using AI, in what could be
a breakthrough for affordable MRI machines and the future of electrified
transport.
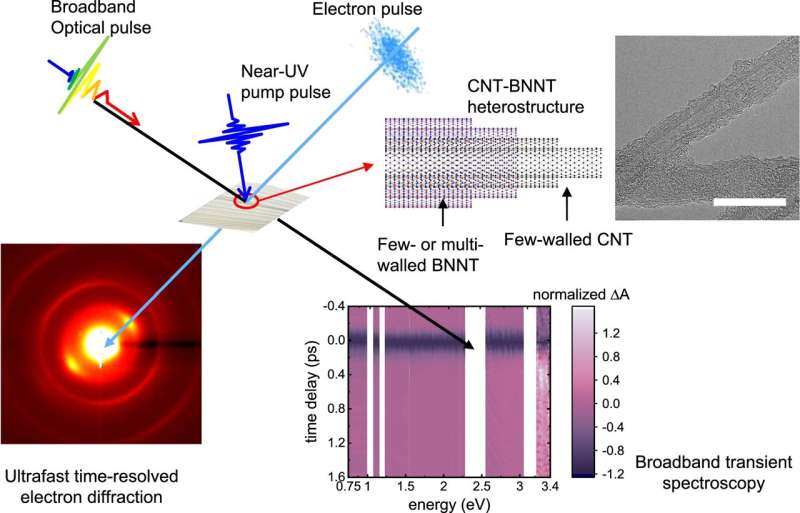
Unveiling novel energy phenomena from light exposure on layered materials (07/06/2024)
Research groups from the
University of Tsukuba and the University of Rennes have discovered a novel
phenomenon in which a nested structure of carbon nanotubes enveloped in boron
nitride nanotubes facilitates a unique electron escape route when exposed to
light. This finding introduces promising avenues for various applications,
including the creation of high-speed optical devices, rapid control of
electrons and other particles and efficient heat dissipation from devices.
New sulfur-free catalyst enables efficient green diesel production (07/06/2024)
Green diesel, a blend of
diesel-grade hydrocarbons derived from renewable oils such as vegetable oils
and animal fats, offers a promising alternative to traditional petroleum
diesel. With a chemical composition similar to petroleum diesel, it integrates seamlessly
into existing engines, making it an environmentally friendly fuel choice that
can significantly reduce CO2 emissions by over 50%.
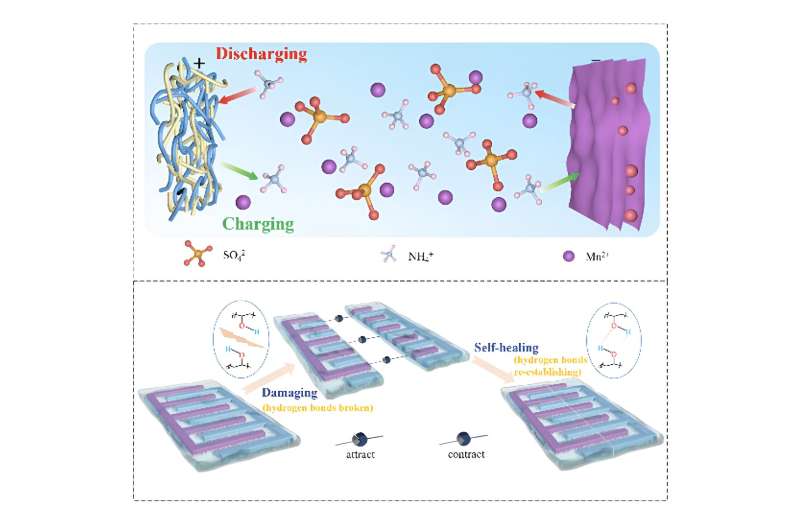
Safer, cheaper, more flexible battery invented for wearable tech (06/06/2024)
Researchers
have developed a safer, cheaper, better performing and more flexible battery
option for wearable devices. A paper describing the "recipe" for
their new battery type was published in the journal Nano Research Energy on
June 3.









