
Researchers develop a laser that produces the strongest ultra-short laser pulses to date (13/10/2024)
The word laser usually conjures
up an image of a strongly concentrated and continuous light beam. Lasers that
produce such light are, in fact, very common and useful. However, science and
industry often also require very short and strong pulses of laser light.

Researchers create a three-dimensional multi-focus laser for glass micro-sculpting (13/10/2024)
Glass materials are widely used
in optical and optoelectronic devices due to their low cost and excellent
mechanical and optical properties. Among them, glass concave/convex linear
structures with feature sizes ranging from several micrometers to hundreds of
micrometers find intensive applications.

New photonics approach enhances quantum computation efficiency (13/10/2024)
A recent study, published in Nature
Photonics, by Prof. Yaron Bromberg and Dr. Ohad Lib from the Racah
Institute of Physics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has made significant
strides in advancing quantum computing through their research on
photonic-measurement-based quantum computation.

Smart new laser technology can monitor greenhouse gases faster, more sensitively (13/10/2024)
Scientists at the National
Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a new laser-based
technique that could dramatically improve our ability to analyze a variety of
materials and gases, including greenhouse gases. This new method, called
"free-form dual-comb spectroscopy," offers a faster, more flexible
and more sensitive way to analyze substances in the air and other materials.

Powerful and compact optical frequency combs provide unique opportunities (13/10/2024)
Remember those big, clunky
machines needed for super precise light measurements? Those days are fading
thanks to tiny devices called microcombs. These chips can do the same job, but
on a much smaller scale, opening doors for new applications.
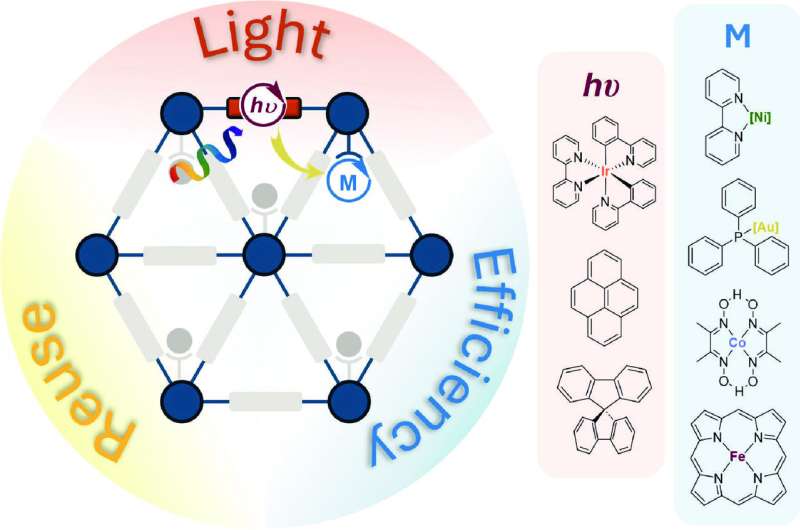
Designing multifunctional framework materials for sustainable photocatalysis (03/10/2024)
The
goal of sustainable chemistry has motivated chemists to use renewable energy in
chemical reactions, minimizing hazardous waste, and maximizing atom economy.
Nature provides a blueprint with photosynthesis, in which carbohydrates are
produced from carbon dioxide and water under sunlight irradiation.
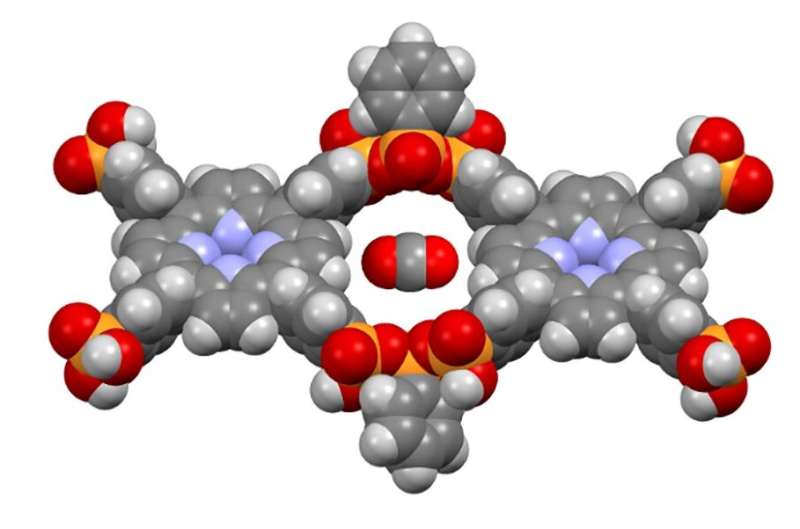
Sustainably produced covalent organic frameworks can be used for efficient CO₂ capture (02/10/2024)
An
international research team headed by Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf
(HHU) and the University of Siegen has synthesized a new compound, which forms
a so-called covalent organic framework. The compound, which is based on
condensed phosphonic acids, is stable and can, for example, be used to capture
carbon dioxide (CO2),
as the researchers describe in Nature
Communications.

Developing plasma-coated paper as a plastic alternative for the packaging industry (02/10/2024)
Plastic waste, harmful to the
environment, has been increasing continually in Germany in recent years.
Packaging generates particularly high volumes of waste. Plant-based coatings
for paper packaging could provide a sustainable alternative in the future.
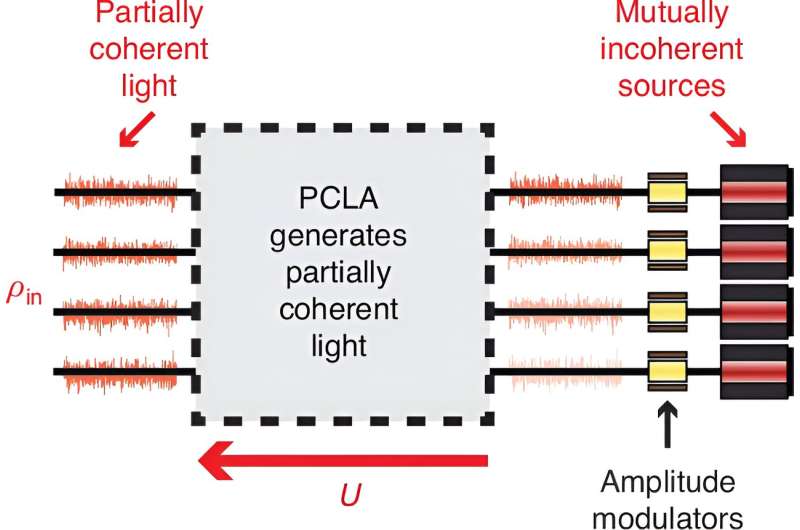
A new apparatus for analyzing partial coherence in integrated photonic networks (30/09/2024)
Anyone familiar with optics labs
is familiar with the extremes of light coherence: laser beams are highly
coherent, producing clear interference patterns used for precise applications
like atomic manipulation or precise sensing. In contrast, light from sources
like flashlights is incoherent, typically unable to produce such patterns
without considerable effort, or at the cost of considerable optical power
losses.
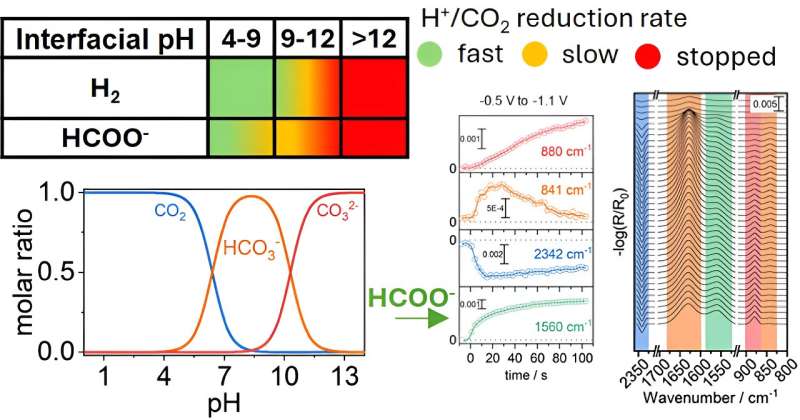
Chemical engineers provide new insights in CO₂ conversion with electricity (28/09/2024)
Researchers from the Department
of Chemical Engineering at the University of Twente, led by Georgios Katsoukis,
have discovered how the chemical environment around copper electrodes can dramatically
influence the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into formate. This discovery can
help improve the selectivity in CO₂ reduction reactions, offering new
insights into how to control these processes more effectively.









